Generation gap
Parents see more benefits to a diagnosis of autism than their affected children do — perhaps unsurprising, given young people’s overwhelming desire to fit in with their peers.
Efforts to ease the symptoms of autism are beginning to ramp up, with promising candidates in various stages of testing.

Parents see more benefits to a diagnosis of autism than their affected children do — perhaps unsurprising, given young people’s overwhelming desire to fit in with their peers.

A compound that activates a pathway related to learning and memory can enhance pair-bonding between prairie voles, according to a study published 7 April in Biological Psychiatry. Enhancing social learning — an individual’s response to social cues — during development could help treat autism.
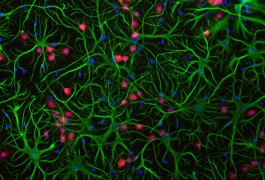
Harmful mutations in a gene that regulates the chemical environment outside of neurons are associated with both autism and epilepsy, according to a study published 31 March in Neurobiology of Disease.

Autism is diagnosed based on the severity and variety of its symptoms. This makes it very difficult to diagnose and easy to confuse with other disorders, such as language delay and intellectual disability, cautions Isabelle Rapin.
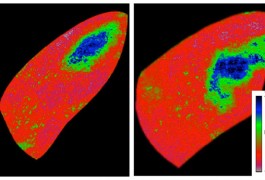
MeCP2, the protein that’s missing or mutated in Rett syndrome, is crucial for remodeling neural circuits in response to vision, according to a study published in April in Neuron.

Genetic screening of children with autism is critical to designing more effective interventions and treatment, says a pediatrician.

Speech-generating devices are a beneficial intervention for people with autism who cannot speak or sign, according to two studies published in the past few months.

Parents of children with autism choose treatment options based on what they believe caused the disorder, according to a French study. More education about autism could help them make better choices.

Adults with autism get better at recognizing faces after they are trained to observe faces as a whole, instead of focusing on individual features, according to a study published 12 April in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.