Video: Microscopy follows neurons in live mouse brains
Wenbao Gan describes the technique he has devised to track the development of neurons in live mouse brains.
Rare or common, inherited or spontaneous, mutations form the core of autism risk.
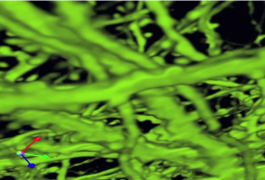
Wenbao Gan describes the technique he has devised to track the development of neurons in live mouse brains.

A subset of people with autism have genetic and biochemical abnormalities in a sleep-related enzyme, according to research presented Friday at a satellite conference of the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

In high-functioning adults with autism, the signal-to-noise ratio in the outer regions of the brain is significantly lower than in healthy controls, according to unpublished research presented Friday in Washington, D.C.

Individuals who have autism show distinct patterns of gene expression in neurological pathways compared with their unaffected siblings, according to unpublished work presented Saturday at the 2011 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Mice missing the Rett syndrome gene MeCP2 show a gradual decline in vision, and too much inhibitory signaling in the visual cortex, according to unpublished research presented Thursday in Washington, D.C.

We’re headed to Washington, D.C. for the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting, and hope to make your lives a little bit easier by reporting on what matters to you.

After analyzing the brains and behaviors of mutant mice and screening genes in people with autism, researchers have pinpointed what they say is a new autism candidate gene: PRICKLE2. The unpublished work was presented Thursday in Washington, D.C.
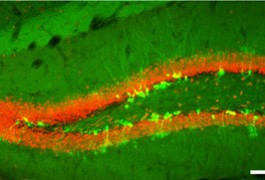
A drug in trials for treating autism-related disorders can reverse memory problems and anxiety in adult mice lacking the schizophrenia gene DISC1 in some cells. The unpublished results were presented yesterday in Washington, D.C.

We’re headed to Washington, D.C. for the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting, and hope to make your lives a little bit easier by reporting on what matters to you.
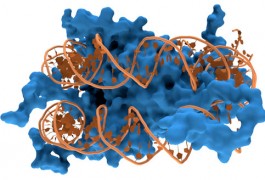
The Rett syndrome gene MeCP2 may subtly regulate the expression of genes across the genome by altering DNA structure.