Study charts epigenetic landscape of autism brains
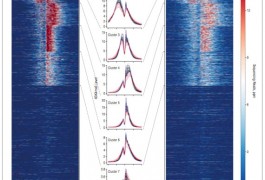
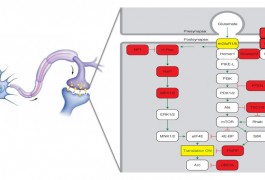
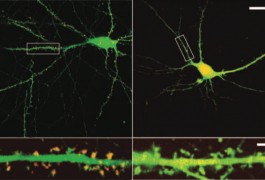
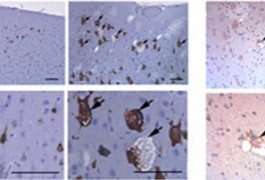
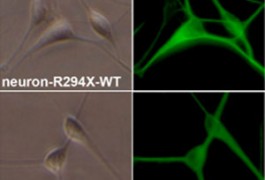
In the brains of some individuals with autism, chemical changes to histones, proteins entwined with DNA, tend to show up near genes linked to the disorder, according to a study published 7 November in the Archives of General Psychiatry.