Genetics: Gene interaction map reveals disease response
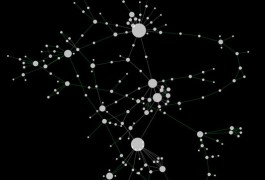
The pattern of interactions among different genes in yeast cells changes in response to disease-like conditions, in this case a DNA-damaging agent, according to a study published 3 December in Science. Mapping epistasis — how various cellular factors work together — is key to understanding complex disorders, such as autism.