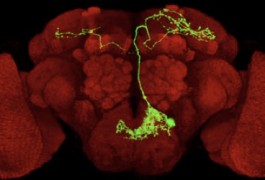
Molecular mechanisms: Scientists debut fruit fly ‘connectome’
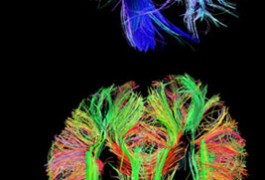
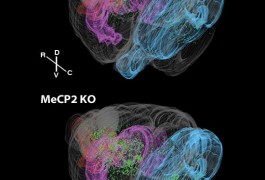
Using tricks of genetic engineering, researchers in Taiwan have created the first comprehensive map of the myriad neuronal connections in the fruit fly brain. The findings appeared 11 January in Current Biology.