Insights for autism from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder show genetic and neurobiological overlap, which may provide clues to the origin of both disorders, says Joel Nigg.
Rare or common, inherited or spontaneous, mutations form the core of autism risk.
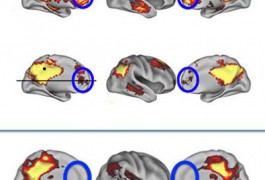
Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder show genetic and neurobiological overlap, which may provide clues to the origin of both disorders, says Joel Nigg.

Duplication of a region on the X chromosome leads to a genetic disorder characterized by severe autism, according to a study published 25 November in Annals of Neurology.

As babies are learning to talk, they shift their focus from speakers’ eyes to their lips, according to a new study that could inform efforts to find an early predictor of autism.
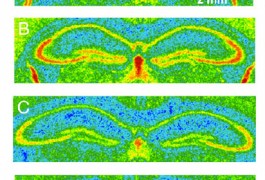
Lithium alleviates the symptoms of fragile X syndrome in mice in part by normalizing protein synthesis in the brain, according to a study published 29 December in Neurobiology of Disease.

A mathematical approach called ‘NEW biology,’ or network-enabled wisdom biology, aims to solve one of the biggest problems in disease research: isolating the key factors that drive diseases from a glut of information.
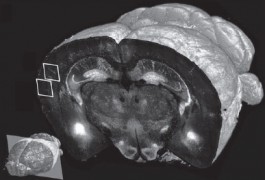
An automated instrument can reconstruct fluorescently labeled mouse brains in less than a day, researchers reported 15 January in Nature Methods.

Two compounds that enhance the activity of BDNF, a protein needed for the growth of neurons, improve motor skills in mouse models of Rett syndrome and increase the mice’s lifespan.
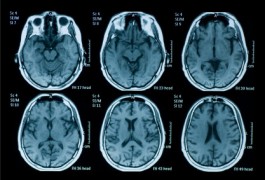
The results of two new studies support recommendations against the use of brain scans to diagnose autism.
Researchers have identified the genetic root of severe mitochondrial disorders in infants whose cases couldn’t be solved by standard genetic testing, according to research published last week in Science Translational Medicine.

A new study uses data from more than 10,000 typical individuals to validate candidate regions implicated in schizophrenia.