Giving fathers oxytocin boosts levels in babies
Two new studies on oxytocin, the so-called ‘trust hormone,’ suggest new avenues for using the drug to treat autism.

Two new studies on oxytocin, the so-called ‘trust hormone,’ suggest new avenues for using the drug to treat autism.
Individuals with autism are more likely than controls to have small, rare duplications or deletions of stretches of DNA in genes that play a role in dampening signals in the brain, according to a study published 2 April in Molecular Autism.

Oxytocin, the so-called ‘love hormone,’ plays a key role in monogamy in rodents, but its association with human relationships is subtle at best.

Individuals with fragile X syndrome make slightly more eye contact in stressful social situations after taking oxytocin compared with placebo.
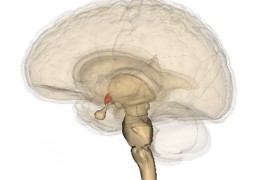
Children with autism have less brain matter than normal in a region that synthesizes the social hormones oxytocin and vasopressin, according to a study published 29 April in Biological Psychiatry.

Children with autism have fewer DNA modifications that regulate gene expression compared with healthy siblings and controls, and show evidence of DNA damage, according to a study published 26 April in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.

Early trauma alters both behavior and gene expression in three generations of mice, suggesting that epigenetic changes may contribute to ‘hidden heritability’ in neuropsychiatric disorders.

Mice that lack the gene for integrin β3, or ITGB3 — which regulates the levels of serotonin in the blood — groom themselves frequently and show less interest in stranger mice compared with controls, according to a study published in February in Autism Research as part of a special issue on mouse models in autism.

A drug already in clinical trials as a tanning compound raises brain levels of oxytocin — a hormone and neurotransmitter involved in social bonding — researchers reported Sunday at the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego. Higher levels of oxytocin can help animals recognize their mates and turn to a friend for help, according to two posters presented at the meeting.
Oxytocin may activate the mirror neuron system — a group of neurons that is active when people empathize with others — according to a paper published in the November Psychoneuroendocrinology.