Immune activation triggers autism features in mice
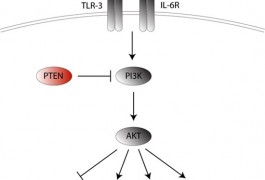
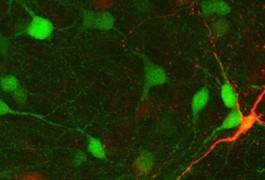
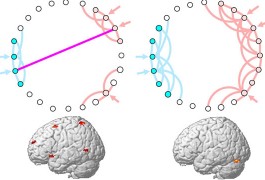
Mice carrying an autism-associated mutation show impaired social interactions and dramatic changes in brain size when their immune systems are activated, according to research presented yesterday at a poster session at the Society for Neuroscience meeting in Chicago.