Genome-wide study fingers first common risk factors for autism
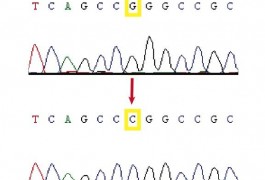
Autism results from a diverse mix of common and rare genetic variants, many of which act in pathways that form and maintain connections between neurons. That’s the message from the largest genome-wide association studies of autism to date, published online today in Nature.