New EEG analysis captures coordination among brain regions
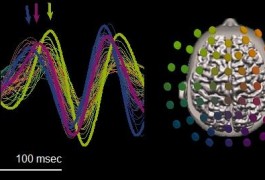
A new way of analyzing the data gathered from electroencephalography (EEG) ― a non-invasive technique that measures brain waves through the scalp ― provides much more information about how brain regions coordinate with one another than standard EEG analysis.