Clinical research: Maternal stress doesn’t trigger autism
Experiencing a stressful event during pregnancy does not increase the risk of having a child with autism, according to an epidemiological study published 13 June in PLoS One.
From parental age to infection during pregnancy, environmental elements can influence autism risk.

Experiencing a stressful event during pregnancy does not increase the risk of having a child with autism, according to an epidemiological study published 13 June in PLoS One.

Identical twins are born with significant differences in the chemical modifications to their DNA, suggesting that the uterine environment can profoundly influence development and risk for disease.
Common variants in three genes involved in the immune system are more likely to crop up in people with autism than in typical controls, according to a study published 9 June in Molecular Autism.

Charles Nelson, who famously showed that social deprivation damages the developing brain, is analyzing brain waves in babies to study how different genetic risk factors might lead to autism.

Pregnant rats exposed to a virus give birth to offspring with significantly altered levels of three proteins important for brain development, according to a study published 9 June in Molecular Brain.

Offspring born to pregnant rats with an activated immune system emit more distress calls when they receive electrical shocks than do controls, according to a study published 9 June in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Understanding the function of neuronal circuits, specifically microcircuits in the prefrontal cortex and elsewhere in the brain, will play a major role in translating research findings into new autism treatments, says Vikaas Sohal.

Researchers have linked the ability to recognize emotions from facial expressions to MET, a well-known autism gene, according to a study published 27 April in PLoS ONE.
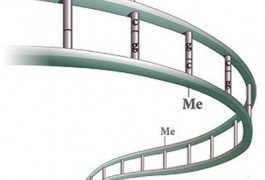
The absence of a chemical alteration called methylation on some stretches of DNA makes them especially prone to mutations, according to a paper published in PLoS Genetics in May.

To find the pathogenic mutations in complex disorders such as autism, researchers may need to conduct sophisticated analyses of the genetic functions that are disrupted, says geneticist Aravinda Chakravarti.