Studies of early development reveal immune link to autism
The molecular soldiers of the immune system may contribute to many cases of autism, according to a diverse array of studies published in the past few months.
From parental age to infection during pregnancy, environmental elements can influence autism risk.

The molecular soldiers of the immune system may contribute to many cases of autism, according to a diverse array of studies published in the past few months.
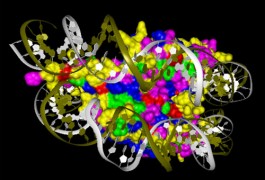
HMGN1, a protein that regulates gene expression, leads to social deficits and hyperactivity when expressed at elevated levels in mice, according to a study published 9 December in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. This effect may result from HMGN1 dampening MeCP2 expression, the study suggests.

Studying the cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie autism is crucial to advancing our understanding of the disorder, says neuroscientist Eric Kandel.
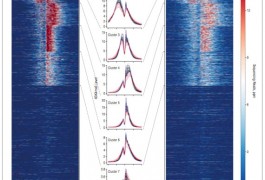
In the brains of some individuals with autism, chemical changes to histones, proteins entwined with DNA, tend to show up near genes linked to the disorder, according to a study published 7 November in the Archives of General Psychiatry.

A drug that blocks a type of receptor at the junctions between neurons reverses repetitive behaviors in a mouse model of autism, according to a new study.
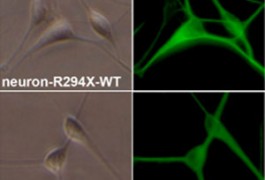
Researchers have derived neurons from stem cells to investigate mutations that lead to Rett and fragile X syndromes.
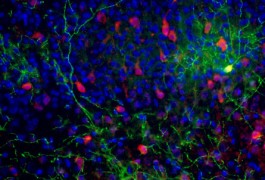
The etiology of autism may be best understood as an impairment of neuronal circuits, specifically interneurons that dampen signals in the brain, says neuroscientist Gordon Fishell.

Altered function of a brain receptor may help explain the why infection during pregnancy raises the risk for schizophrenia in the offspring, according to an unpublished rat study presented at the 2011 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
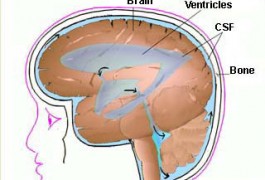
A small fraction of young children with autism have low levels of folate, a B vitamin, in their cerebrospinal fluid, according to unpublished research presented at the 2011 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
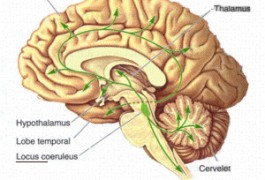
Drugs that act on the adrenaline system can alleviate autism-like symptoms in a rat model of the disorder, according to unpublished research presented Sunday in Washington, D.C.