Molecular mechanisms: Drug corrects excitable mouse brains
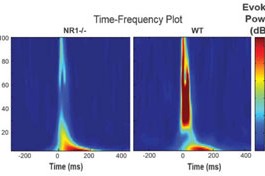
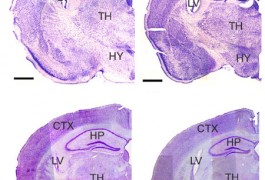
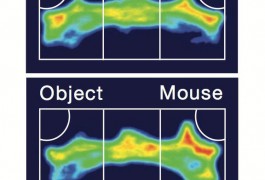
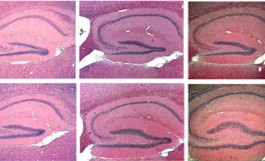
A compound called baclofen restores the balance between different types of brain signals and alleviates autism-like behaviors in mice, according to a study published 17 July in Translational Psychiatry. A similar drug called arbaclofen is in clinical trials as a treatment for autism and fragile X syndrome.