Norway baby study expected to yield insights into autism
The Autism Birth Cohort, based on data from 100,000 Norwegian children and their families, aims to uncover genetic and environmental factors contributing to the disorder.
Autism’s core symptoms accompany a constellation of subtle signs that scientists are just beginning to unmask.

The Autism Birth Cohort, based on data from 100,000 Norwegian children and their families, aims to uncover genetic and environmental factors contributing to the disorder.

You’ll never hear Jacqueline Crawley talk about an ‘autistic mouse’. In fact, in her keynote address at IMFAR in May, she implored the audience to never use those two words in the same sentence.

If you believe the hype about oxytocin, it’s nothing short of a wonder drug: it can make you trust a stranger, enhance a mother’s bond with her child and, according to a study published earlier this year, improve social skills in individuals with autism. But look more closely, and there is ample cause for caution.
With robust training in developmental psychology and a techie’s fervor for new tools, Kevin Pelphrey is systematically investigating how the brain changes during development — starting in infants as young as 6 weeks old.
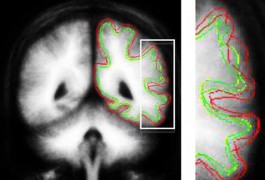
An imaging study widely interpreted as heralding a diagnostic brain scan for autism is more preliminary than popular media reports would indicate, according to experts familiar with the work.
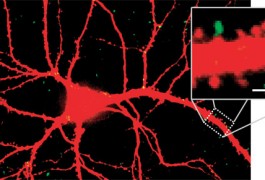
Researchers have uncovered an important molecular piece of a learning mechanism that occurs at the junction between neurons. The findings, which may help understand how the brain is disrupted in disorders such as autism, appear in the 24 June issue of Neuron.
In the not-too-distant future, we may be able to diagnose toddlers with autism using a simple clinical test — based on voice patterns, blood or even urine.
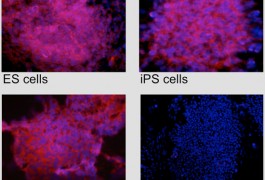
Not all stem cells are created equal, a string of new studies suggests: adult cells that are reprogrammed into stem cells carry chemical remnants of the tissue from which they originate, making them distinct from embryonic stem cells. These differences may have important implications for studying fragile X syndrome and other diseases that arise from epigenetic glitches.

Racial minorities are under-represented in genetic studies, in part because research guidelines do not account for differences in family structure, according to a report based on statistics from several autism gene banks. In response to the report, research teams at Stanford University and the University of California, Los Angeles, are revamping their recruitment practices.

One of the largest genome-wide association studies for autism spectrum disorders, reported last week in Human Molecular Genetics, allows only one definitive conclusion: it isn’t large enough.