Genetics: De novo mutation rate higher in autism
Spontaneous harmful mutations are more frequent in individuals with autism and schizophrenia, according to two studies published in September.
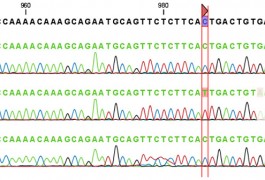
Spontaneous harmful mutations are more frequent in individuals with autism and schizophrenia, according to two studies published in September.

At 6 months of age, siblings of children with autism are less likely to gaze spontaneously at their caregivers while focused on learning a new task, though they learn the task just as quickly as do low-risk infants, according to a study in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.

Telling jokes allows children to connect with others, refine their language skills and develop keen imaginations. Because these are precisely the skills lacking in people with autism, studying humor in children with the disorder may give insights into their abnormal brain circuitry and even lead to therapies, according to a review published in the Journal of Child Neurology.

Children with autism are less likely to yawn when others do, perhaps because they tend not to unconsciously mimic behavior.

Individuals with autism detect the motion of an object with the same accuracy as they detect the motion of people, whereas controls are more attuned to human movement, according to a study published in August in Autism Research.
A common variation within a region on chromosome 16 puts a large proportion of the general population at risk for intellectual disability, according to a study published in August in Nature Genetics.
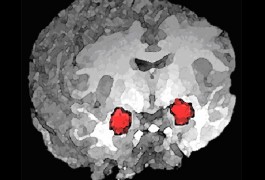
Damage to the amygdala — a region of the brain that regulates emotional processing — does not cause autism, according to a study of two individuals with lesions in the region. The study, published in September in the Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, found that these individuals show no evidence of autism when given multiple diagnostic tests.
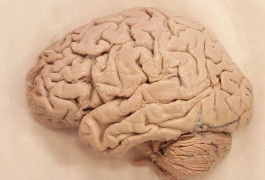
A study of postmortem brain tissue shows that RPP25, a gene on the autism-linked 15q22-26 chromosomal region, is expressed differently in the brains of people with the disorder. This is the first time this gene has been implicated in autism.
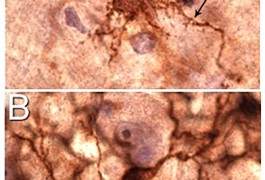
A study of postmortem tissue shows that microglia, cells that provide immune protection to the brain, are altered in the brains of individuals with autism.

Genes responsible for Alzheimer’s disease and fragile X syndrome — a form of mental retardation linked to autism — may operate through the same pathway, according to a study published in The Journal of Neuroscience.