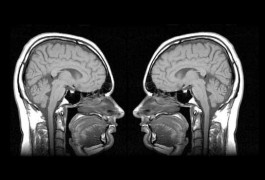
Autism brains characterized by fewer excitatory neurons
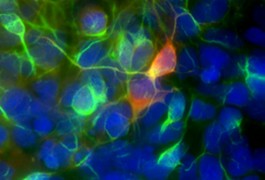
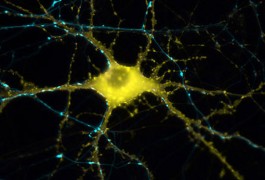
People with autism have structural differences in the temporal cortex — a brain region involved in sound and language processing — compared with controls, according to a postmortem study presented Monday at the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego.