‘Thunder’ promises lightning-fast analysis of big brain data
Researchers have developed a set of software tools called Thunder that can find meaningful patterns in large-scale data on brain activity.
Researchers have developed a set of software tools called Thunder that can find meaningful patterns in large-scale data on brain activity.
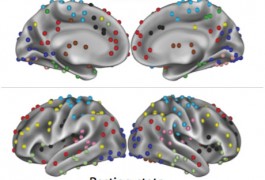
Researchers measure how brain networks work together by scanning volunteers’ brains either while they’re resting passively or while they’re engaged in a task. A study published 2 July in Neuron argues that the networks activated in these two scenarios are more similar than previously thought.

A new device designed to conduct magneto-electroencephalography in children younger than 3 years is ideal for detecting early signs of autism, researchers reported 3 March in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.

Thought until recently to only coordinate motor skills, the cerebellum is involved in diverse cognitive functions such as language and social interaction, and may play a role in autism, says Emanuel DiCicco-Bloom.

People with autism show diminished language activity in the left halves of their brains but otherwise show typical specialization between hemispheres, according to a study published 6 February in Molecular Autism.

Treatment with the hormone oxytocin boosts brain activity and improves recognition of emotions in people with autism, according to two small studies published in February.
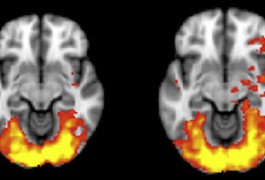
When exposed to irritating noises or images, children with autism show hypersensitivity in brain regions that process sensory information and emotions, according to a study published in November in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.

Three studies published over the past two months have found significant evidence that children and adolescents with autism have brains that are overly connected compared with the brains of controls. The findings complicate the theory that autism is fundamentally characterized by weakly connected brain regions.

Oxytocin, the infamous ‘love hormone,’ may attune the brains of people with autism to respond to social information such as facial expressions, researchers reported 2 December in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study boosts oxytocin’s promise for treating the social deficits seen in autism.

Studies at the level of neural circuits are needed to better understand the importance of both increased and decreased connectivity between different regions in the autism brain, say John Rubenstein and Vikaas Sohal.