Disparities in autism diagnosis may harm minority groups
Clinicians are underdiagnosing autism in children from low-income families and minority groups — setting back their potential to benefit from therapy.

Clinicians are underdiagnosing autism in children from low-income families and minority groups — setting back their potential to benefit from therapy.
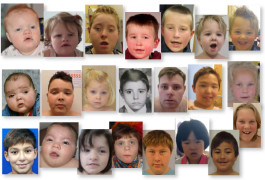
Mutations in a gene called POGZ lead to a constellation of traits, including a small head, developmental delay and, often, autism.

After a steady climb since 2000, the prevalence of autism among school-age children appears to have stalled at 1 in 68.

Terms such as ‘low-functioning’ often used to describe people with autism, are misleading and stigmatizing. Tracking people’s daily lives over time may offer a clearer picture of life with the condition.

Most children who have both autism and intellectual disability take their first steps on time or earlier than those with other conditions.

A third strain of mice carrying an autism-linked mutation captures the nuances of this structural mutation in people.

The authors of “Neurotribes” and “In a Different Key” urge scientists to question their biases and to translate their findings into tangible benefits for those on the spectrum.
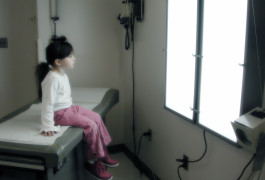
A new collection stores genetic and behavioral information about children with autism in inpatient psychiatric units.
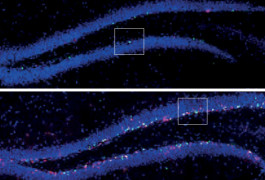
Electrically stimulating a particular circuit in the brain shows promise for reversing symptoms of Rett syndrome, a disorder that shares features with autism.

Researchers have defined a new syndrome that results from carrying two mutated copies of CNTNAP2, a gene linked to autism.