Autism, developmental delay can have distinct genetic origins
Mutations in certain genes contribute specifically to autism, and others only to developmental delay.

Mutations in certain genes contribute specifically to autism, and others only to developmental delay.

Since the DSM-5’s debut, schoolchildren have gained stronger legal rights and better opportunities for accessing services; for adults, it’s a different story.

The move to replace ‘mental retardation’ with ‘intellectual disability’ is widely accepted, but little data exist on the impact of this change.

Five years after its latest revision, the manual used to diagnose autism is back under scrutiny, as evidence suggests it excludes some people on the spectrum.
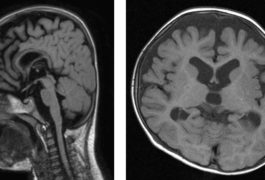
Mutations in a gene called ADNP lead to a syndrome that includes autism, intellectual disability and problems with the gut, eyesight, heart and brain.

Children with autism typically have four or five other conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, that can affect when they are diagnosed.
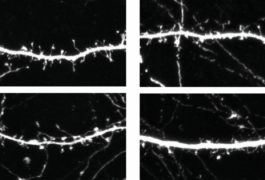
A single gene, OTUD7A, may account for most of the features seen in people missing a segment of chromosome 15 known as 15q13.3.

A semirural Colombian town called Ricaurte is home to the largest recorded genetic cluster of people with mutations linked to fragile X syndrome.

People with autism who are admitted to the hospital for self-injury tend to have low intelligence quotients and severe repetitive behaviors.

Spontaneous mutations that impair proteins may lead to motor problems in children with autism.