Study maps brain coordinates of language delay in autism
A new analysis of 22 studies points to a possible anatomical source for some of the language problems in autism.
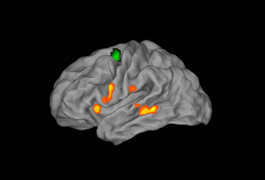
A new analysis of 22 studies points to a possible anatomical source for some of the language problems in autism.

Children with autism fear the unknown and react negatively when faced with unpredictable situations. This intolerance of uncertainty is closely tied to anxiety but may manifest independently.

Children with autism who have trouble learning to sit up, crawl or walk also tend to have difficulty learning to speak and understand words.
A scientist gets permission to edit the genomes of human embryos, and researchers argue that it’s time to leave race out of genetic studies.
A new collection stores genetic and behavioral information about children with autism in inpatient psychiatric units.
As powerful genetic tools identify increasing numbers of autism genes, scientists are parsing the pool of autism into new syndromes, each with a distinct genetic origin.

Nearly half of siblings of children with autism have difficulties with attention, language, learning or mood.

A study of more than 2,500 families that have at least one child with autism has found three factors that predict autism symptoms in an unaffected sibling.

Some restricted and repetitive behaviors may have hidden benefits for people with autism, so scientists should work to find a happy medium between acceptance and change.
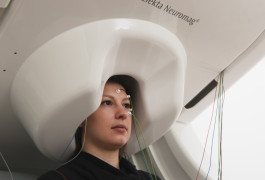
Delayed activation of brain areas governing speech could contribute to the language difficulties some people with autism experience.