Great sequencing power — great responsibility
Chris Gunter and Daniel MacArthur discuss guidelines for assessing the evidence that a genetic variant causes autism or another disorder.

Chris Gunter and Daniel MacArthur discuss guidelines for assessing the evidence that a genetic variant causes autism or another disorder.

Mutations in a gene associated with DNA packaging may lead to autism and intellectual disability, suggests a study published 16 February in Nature Genetics.
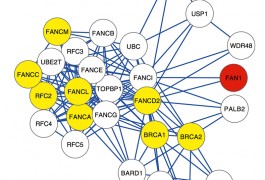
Mutations in FAN1, a gene in the 15q13.3 chromosomal region, raise the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders including autism and schizophrenia, according to a new study published 7 January in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

Mutations in a single gene in 15q11.13 — a chromosomal region linked to multiple neurological disorders — may increase the risk of autism, according a study published in November in Nature Genetics.
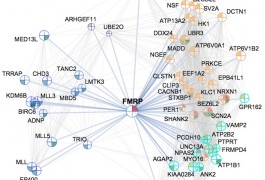
Now that genetic studies have implicated several hundred genes in autism, researchers are turning their attention to where and when in the healthy young brain these genes are expressed. The first two studies to tackle these questions appear today in Cell.
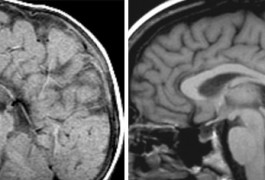
The largest genetic analysis yet conducted of people lacking a brain structure called the corpus callosum shows that the condition shares many risk factors with autism. The study was published 3 October in PLoS Genetics.

An effort to rank autism genes on the strength of the evidence implicating them in the disorder will provide researchers with a focused list of genes to study, says Alan Packer.
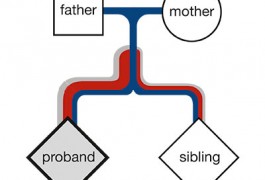
Two new studies have found more small deletions and duplications of DNA in individuals with autism than in unaffected controls. These variants may also affect the severity of the disorder.

One of the largest genome-wide screens of methyl tags in postmortem brains has found that people with autism have three unique regions of methylation — chemical modifications that affect gene expression. The results were reported 3 September in Molecular Psychiatry.

A new statistical model pulls together information about inherited and spontaneous mutations in a single analysis to enhance the search for autism candidate genes. The method, called transmission and de novo association, or TADA, was described 15 August in PLoS Genetics.