Picking priorities; wristband recorder; going for gold
People with autism assemble a wish list for researchers, a digital wristband tracks anxiety, and a runner on the spectrum prepares for his Paralympic debut.
People with autism assemble a wish list for researchers, a digital wristband tracks anxiety, and a runner on the spectrum prepares for his Paralympic debut.
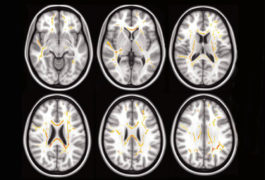
Children with autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder all show similar disruptions in brain structure.

Men with autism who have above-average intelligence may not achieve typical financial and personal milestones — but many are content.
A study links acetaminophen use to autism, scientists find a flaw in brain imaging software, and a television show about autism is set to premiere next week.

Mental health conditions crop up more than twice as often in families that include a child with autism as in the general population.

Some children are highly sensitive to sound, sight or touch, whereas others seem almost numb. Exploring the differences may offer insights into autism.
Proposed changes to federal ethics rules spark concerns among researchers, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder may be different in adults, and an artist plans to print a three-dimensional hand using stem cells.
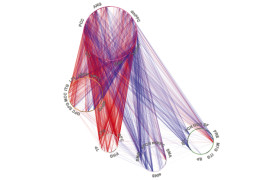
A new set of charts shows how brain connections can change as children grow, and can serve as a reference for detecting problems with attention.

A new algorithm relies on abilities rather than diagnoses to steer clinicians toward personalized treatments for autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
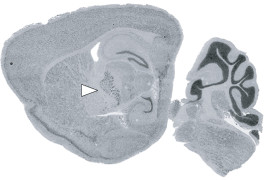
Mice missing a gene called PTCHD1 in a deep-seated brain structure have autism-like symptoms that ease with treatment.