Imaging studies investigate language circuits in autism
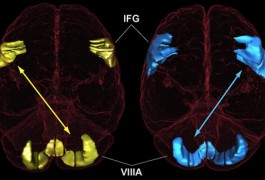
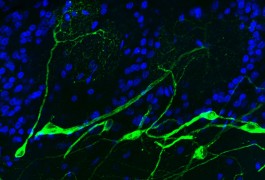
Some brain areas involved in speech are larger and some smaller in children with autism compared with healthy controls, according to a series of imaging studies conducted by a Boston research group.