Fragile X models give clues to stem cell programming
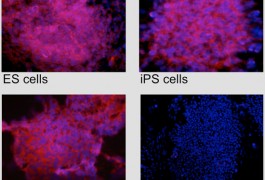
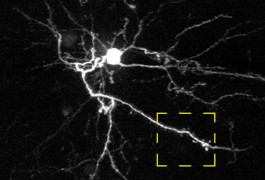
Not all stem cells are created equal, a string of new studies suggests: adult cells that are reprogrammed into stem cells carry chemical remnants of the tissue from which they originate, making them distinct from embryonic stem cells. These differences may have important implications for studying fragile X syndrome and other diseases that arise from epigenetic glitches.