Study links autism to stem cell development
The molecular defects that cause some cases of autism may arise during the development of neuronal stem cells, according to a new theory bolstered by several independent animal and human studies.
Autism’s core symptoms accompany a constellation of subtle signs that scientists are just beginning to unmask.
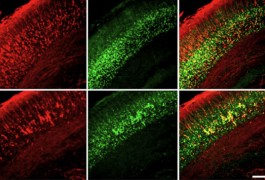
The molecular defects that cause some cases of autism may arise during the development of neuronal stem cells, according to a new theory bolstered by several independent animal and human studies.

Children with autism rely on conscious planning, rather than habit, to control their movements, according to the first brain imaging study to examine motor performance in the disorder.
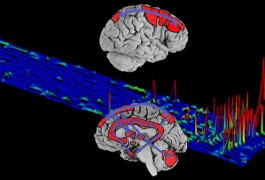
Applying an emerging technique that combines genetic data and brain scans, researchers have identified two new genes involved in schizophrenia. The method, called ‘imaging genetics’, holds promise for linking genes to brain function in complex psychiatric disorders, including autism.

The answer to a long-standing mystery in visual neuroscience may also help explain how people with autism perceive faces, according to a study published in March in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
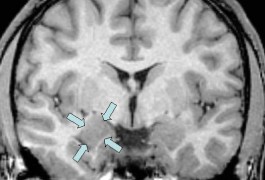
The characteristic inability of a person with autism to respond to emotions may stem from sustained arousal in the amygdala, the brain region needed to interpret emotions from facial expressions.

The genetic culprit in fragile X syndrome — a form of mental retardation frequently accompanied by autism — can alter how much fruit flies sleep, according to a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience.

Most young animals, from newly hatched chicks to 2-day-old humans, are exquisitely sensitive to the movements of other animals. But 2-year-old children with autism don’t pay special attention to this so-called ‘biological motion’, according to a study published today in Nature.
In the spring of 2002, as a new graduate student at the University of Washington, Raphael Bernier was charged with introducing his advisor, Geraldine Dawson, before her lecture to a room of about 40 people from the psychology department. To Dawson’s astonishment, Bernier sang his introduction to the tune of On Top of Old Smokey. “[It was] a pretty gutsy thing for a first-year student to do,” Dawson says.

In the late 1990s, after Daniel Geschwind had established himself as an expert on the genetics of neurological diseases, a personal connection abruptly pulled him into autism research. Since then, he has participated in dozens of studies probing the genetic basis of autism and related neuro-developmental disorders.
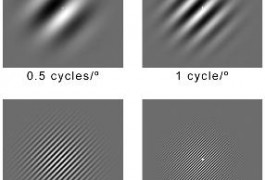
‘Eagle-eyed’ vision, characteristic of many people on the autism spectrum, stems at least in part from abnormal variations in the early stages of visual processing, according to two reports published in the January issue of Biological Psychiatry.