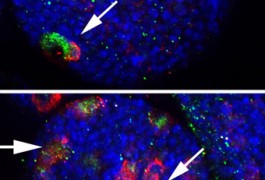
The power of talk
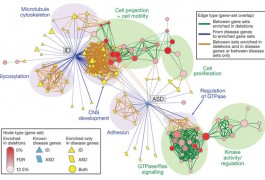
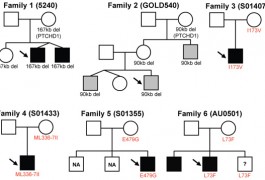
In order to understand the interaction between genes and environment in autism, researchers in different disciplines will have to move back and forth between those two realms, stretching out of their intellectual comfort zones. But if the mood at an interdisciplinary workshop two weeks ago is any indication, that challenge is also a source of excitement.