Diagnosis
A new look at walking in early childhood: Q&A with Rujuta Wilson
Quantifying toddlers’ gaits promises to improve autism diagnosis and intervention.
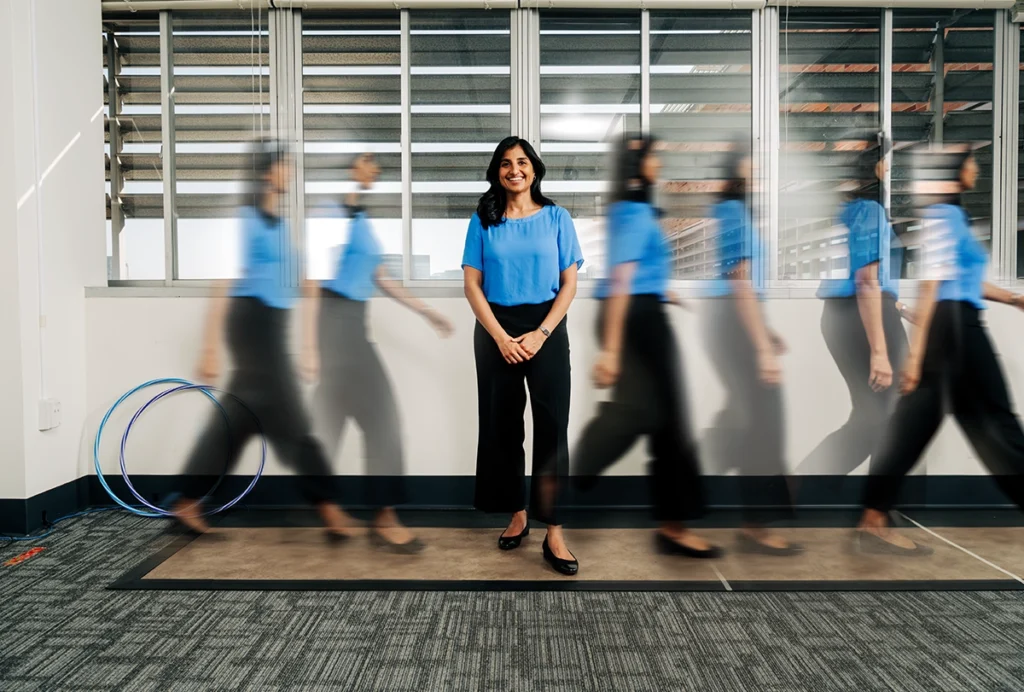

A new look at walking in early childhood: Q&A with Rujuta Wilson
Mutation in top autism-linked gene may alter eye reflex
The discovery could help clinicians diagnose children who carry mutations in the gene, called SCN2A, and gauge their responses to potential therapies.
Mutation in top autism-linked gene may alter eye reflex
‘Prototypical autism’ research is likely a dead end
Efforts to define “frank” or “classic” forms of the condition build on several assumptions that the science has not yet borne out.

‘Prototypical autism’ research is likely a dead end
New tablet-based tools to spot autism draw excitement — and questions
Handheld devices promise to bring autism detection home, but many researchers urge caution.
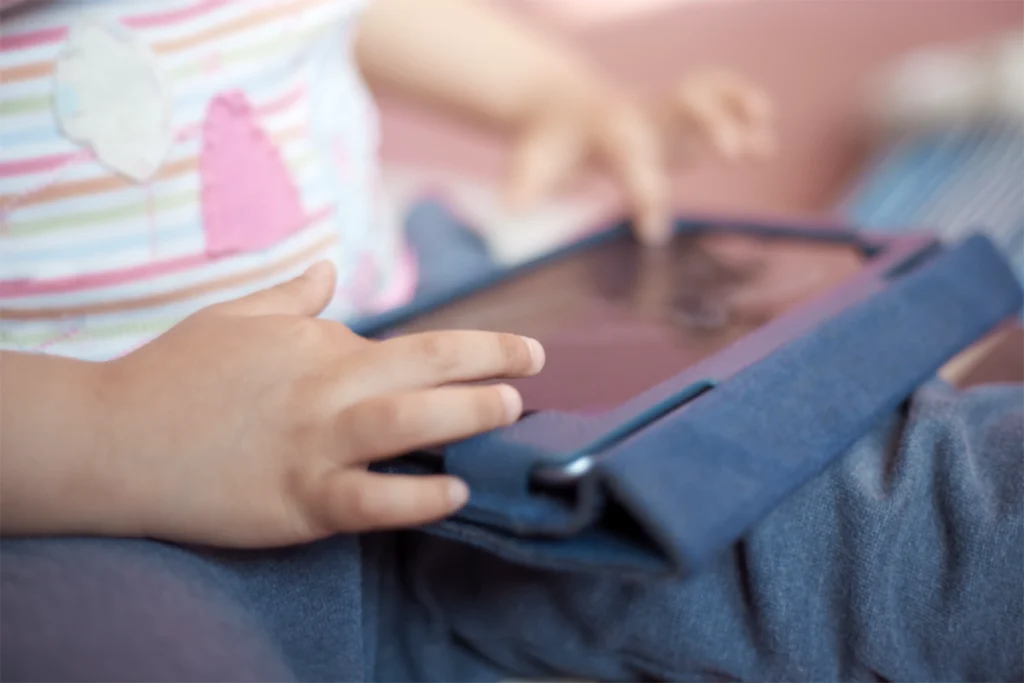

New tablet-based tools to spot autism draw excitement — and questions
Year in Review: Spectrum’s best in 2023
Here are five must-reads from our coverage of autism research over the past 12 months.
Autism research hits the road
Some scientists are thinking creatively about how to collect data in flexible environments and meet communities where they’re at.
Teasing apart insistence on sameness with Mirko Uljarević
The hallmark autism trait has multiple facets, Uljarević and his colleagues have found.

Teasing apart insistence on sameness with Mirko Uljarević
Journal club: Why do some children lose their autism diagnosis?
More than one-third of a cohort of autistic toddlers no longer meet criteria for the condition at school age, according to a new study, but the findings may not generalize because the cohort is predominantly white and affluent.

Journal club: Why do some children lose their autism diagnosis?
Looking at eye tracking’s potential for clinical trials
This month’s Going on Trial newsletter explores how eye tracking might be used beyond helping with diagnosis, among other drug development news.
Looking at eye tracking’s potential for clinical trials
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
An imbalance in the number of excitatory neurons in early brain development may account for the difference.
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
Explore more from The Transmitter
Neuroscience needs a research-video archive
Video data are enormously useful and growing rapidly, but the field lacks a searchable, shareable way to store them.
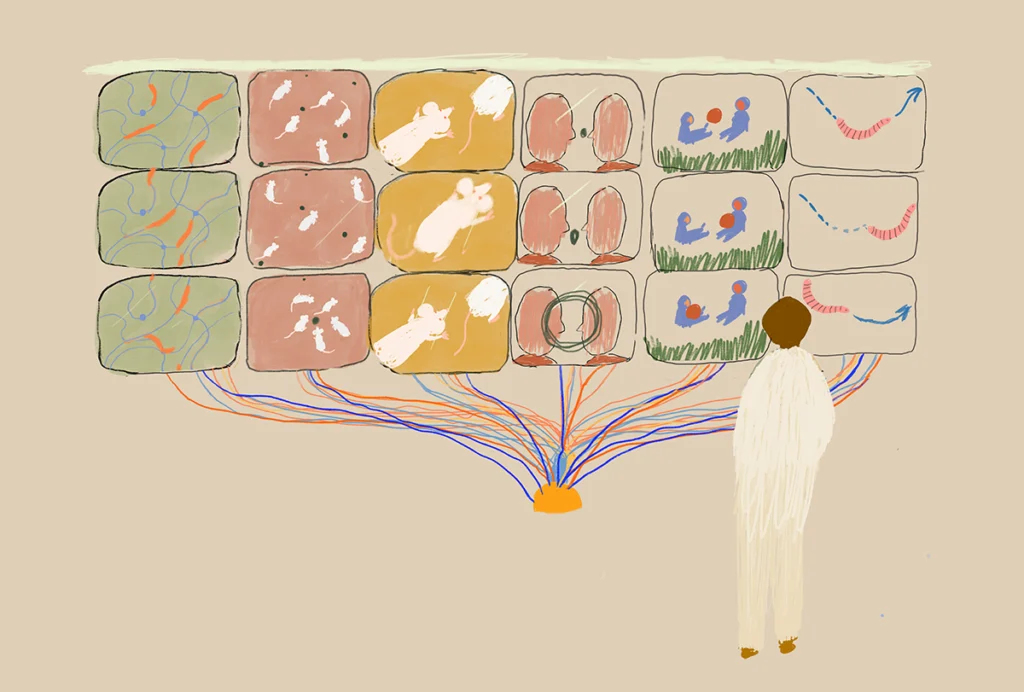
Neuroscience needs a research-video archive
Video data are enormously useful and growing rapidly, but the field lacks a searchable, shareable way to store them.
Inclusivity committee disbands in protest at Canadian neuroscience institute
The majority of an 11-person committee resigned from the group this week following news that a staff position overseeing equity, diversity and inclusion would not be renewed.

Inclusivity committee disbands in protest at Canadian neuroscience institute
The majority of an 11-person committee resigned from the group this week following news that a staff position overseeing equity, diversity and inclusion would not be renewed.
How to explore your scientific values and develop a vision for your field
As a new professor, I was caught off guard by one part of the job: my role as an evaluator.
How to explore your scientific values and develop a vision for your field
As a new professor, I was caught off guard by one part of the job: my role as an evaluator.
