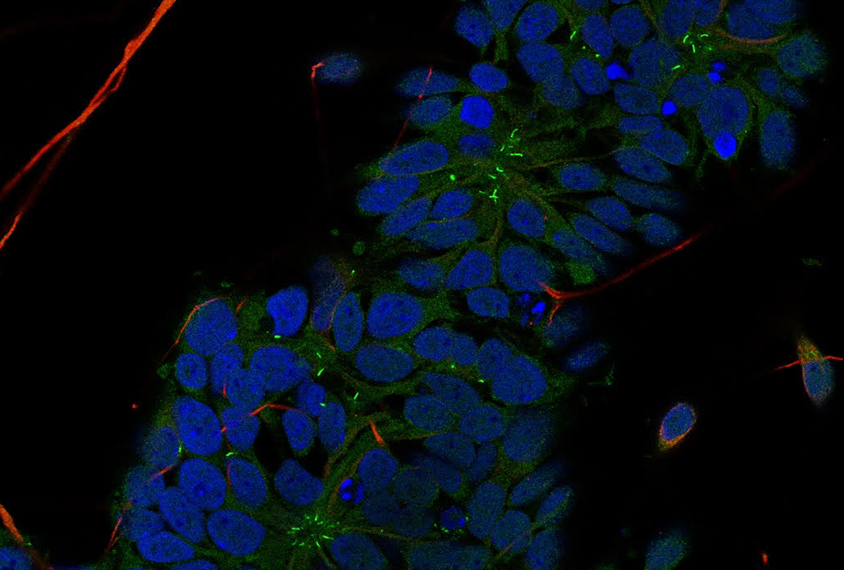
Stem cells
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Faulty mTOR signaling, implicated in syndromic forms of autism, also hinders cells grown from people with idiopathic autism or autism-linked deletions on chromosome 16.
Autism subgroups converge on cell growth pathway
Building a brain: How does it generate its exquisite diversity of cells?
High-throughput technologies have revealed new insights into how the brain develops. But a truly comprehensive map of neurodevelopment requires further advances.

Building a brain: How does it generate its exquisite diversity of cells?
Raising the bar for stem cell research: Q&A with Jack Mosher
New quality benchmarks for basic research involving stem cells promise to improve rigor and reproducibility, says Mosher, who helped develop the standards.
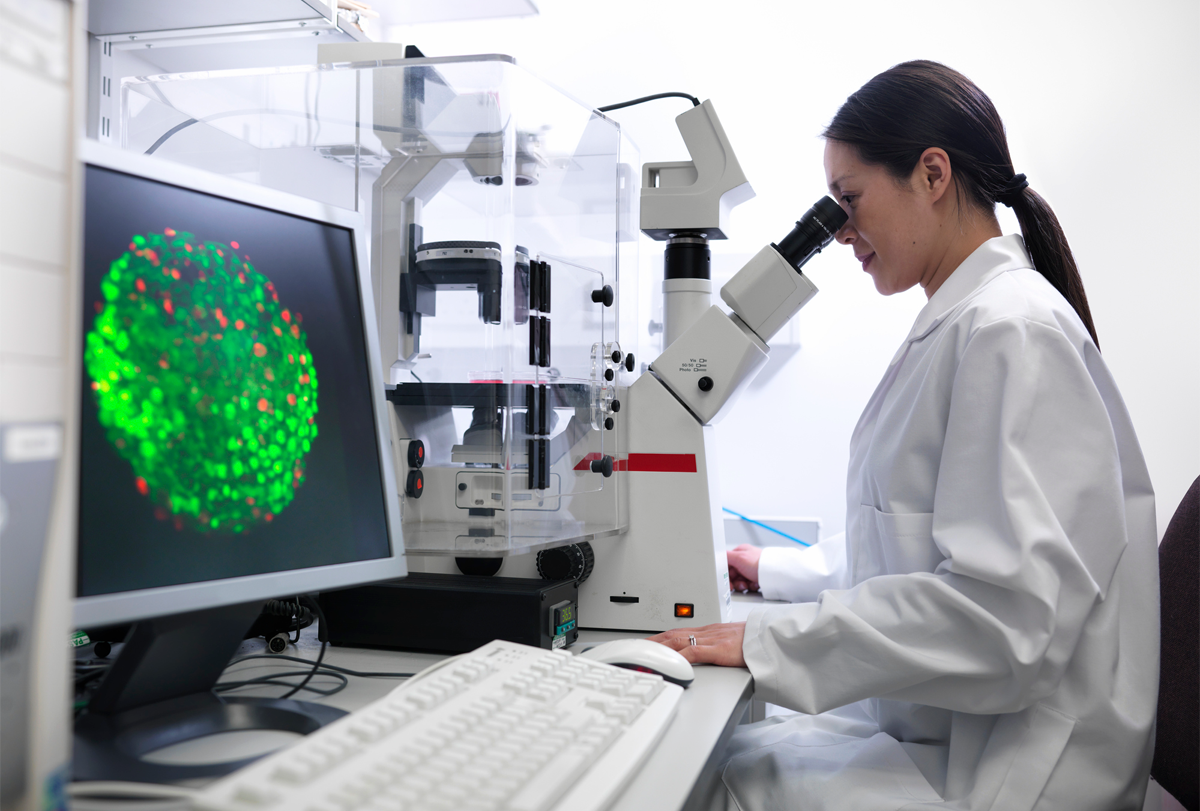

Raising the bar for stem cell research: Q&A with Jack Mosher
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Astrocytes fuel erratic firing in fragile X neurons
A shift in astrocyte secretions may explain the atypical firing patterns of neurons derived from people with fragile X syndrome.
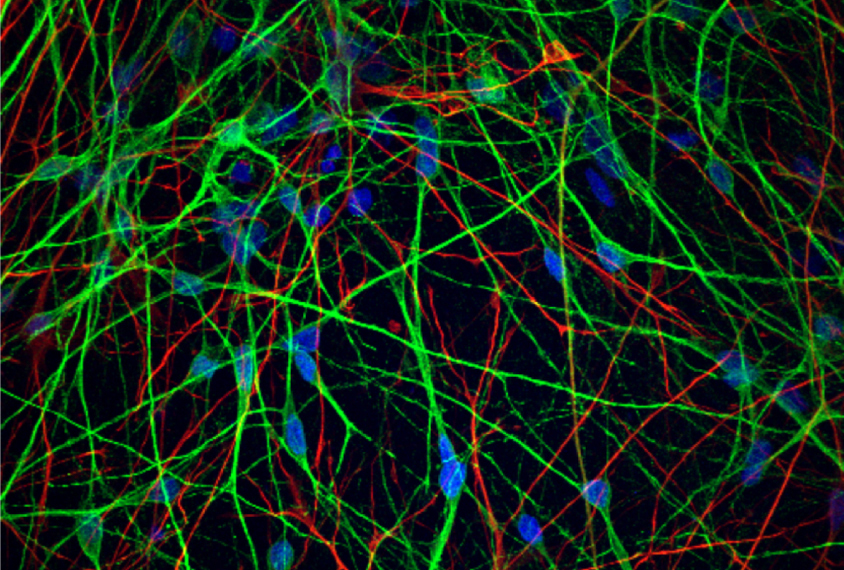
Astrocytes fuel erratic firing in fragile X neurons
‘Splice-switching’ strategy boosts SYNGAP1 expression
The approach improves the function of SYNGAP1-deficient neurons in vitro, but whether it will work in people remains unclear.
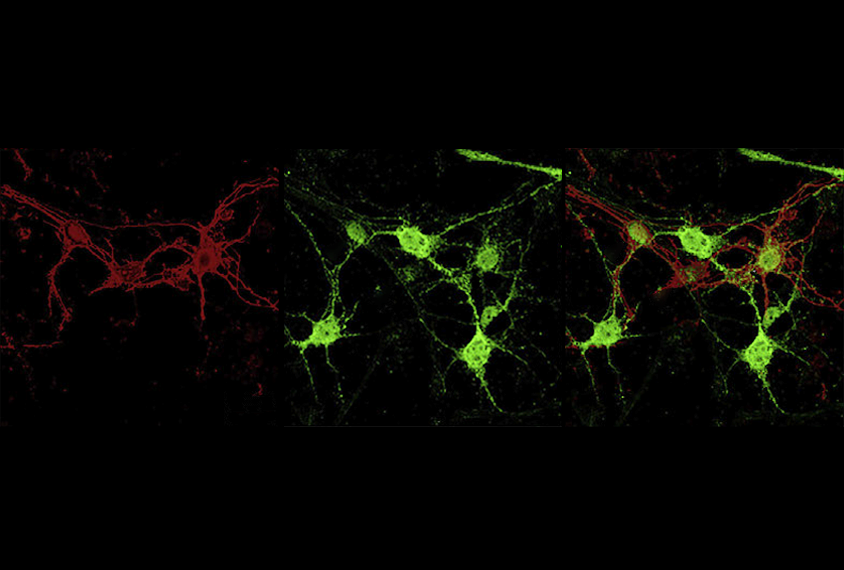
‘Splice-switching’ strategy boosts SYNGAP1 expression
Autism-tied gene ZNF462 keeps developing neurons on track
The gene, linked to a little-known condition called Weiss-Kruszka syndrome, prevents embryonic stem cells from deviating from their neuronal destiny.
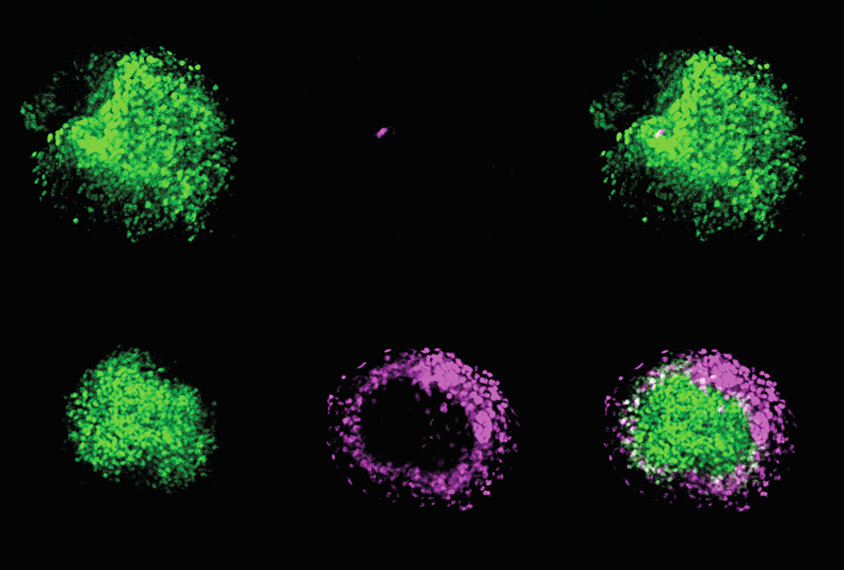
Autism-tied gene ZNF462 keeps developing neurons on track
Autism and the cell’s antennae
Many autism-linked genes are somehow tied to cilia, the tiny hair-like sensors that stud a cell’s surface. But the question remains whether, and how, cilia differences contribute to the condition.
‘Assembloids’ lay bare autism-linked genes that hamper neuron development
The model enables the study of autism-linked genes at the earliest stages of neural development.
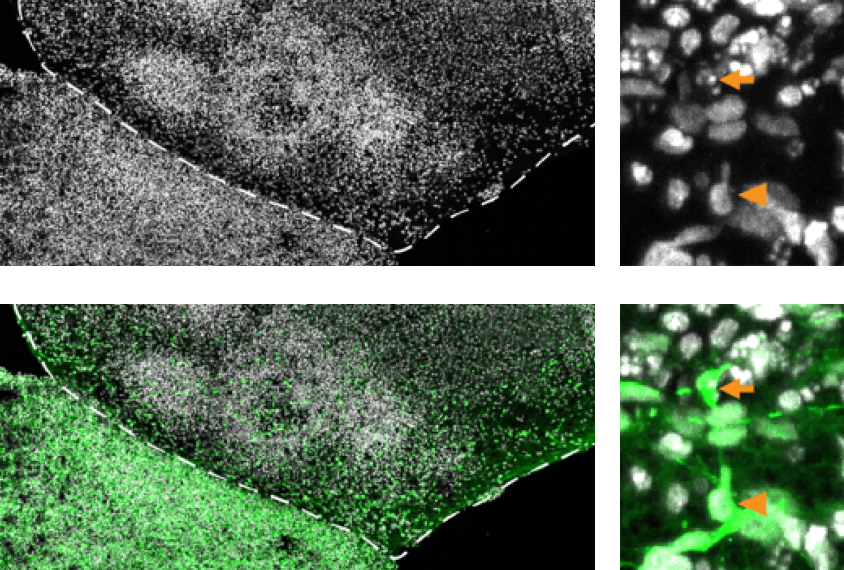
‘Assembloids’ lay bare autism-linked genes that hamper neuron development
Lab-grown ‘embryoids’ offer new window into gene-trait relationships
The developmental models have advantages over natural embryos and other synthetic models, such as organoids, but present technical and ethical challenges.
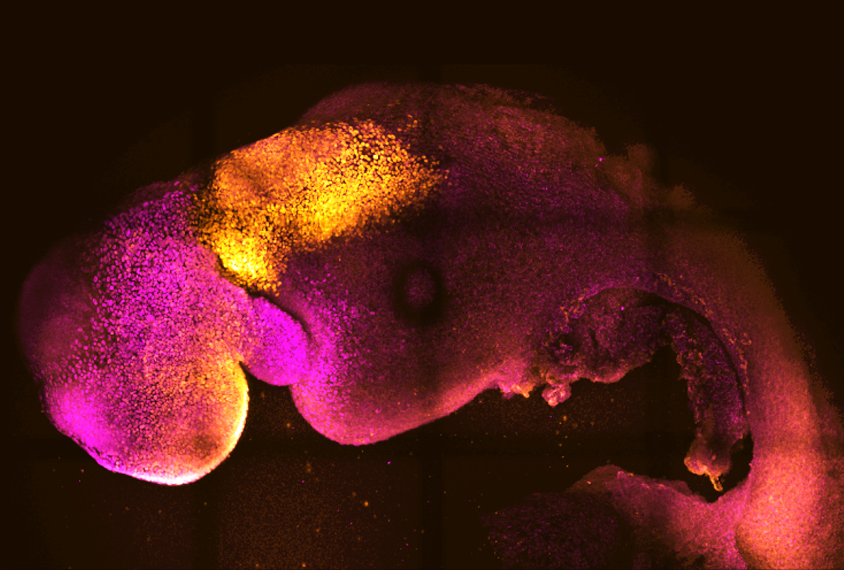
Lab-grown ‘embryoids’ offer new window into gene-trait relationships
Explore more from The Transmitter
Cocaine, morphine commandeer neurons normally activated by food, water in mice
Confirming a long-held hypothesis, repeated exposure to the drugs alters neurons in the nucleus accumbens, the brain’s reward center, and curbs an animal’s urge for sustenance.
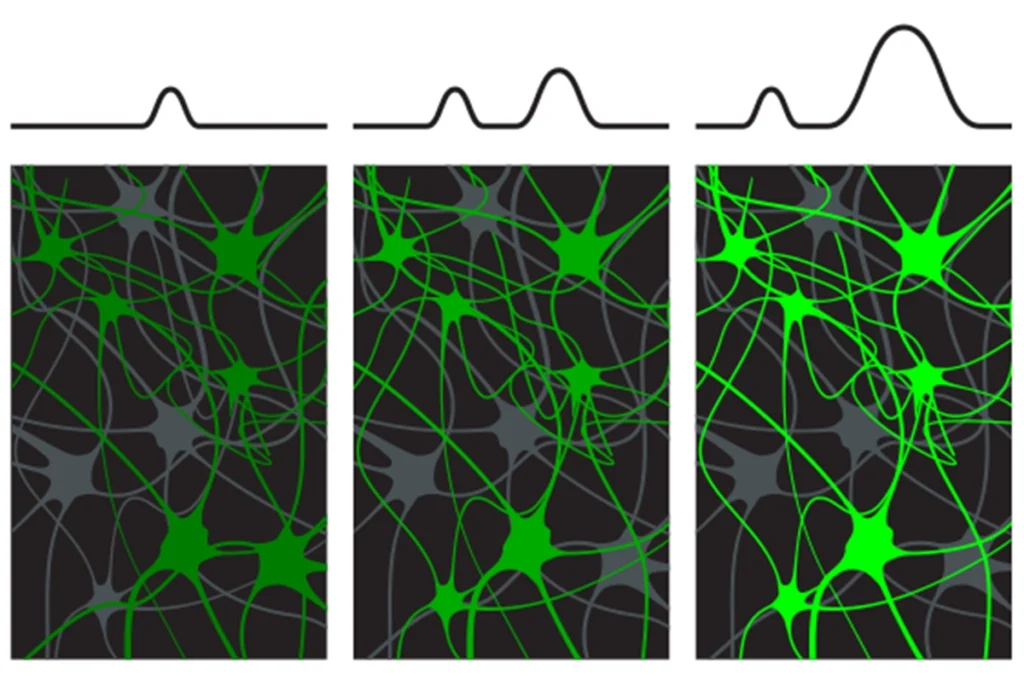
Cocaine, morphine commandeer neurons normally activated by food, water in mice
Confirming a long-held hypothesis, repeated exposure to the drugs alters neurons in the nucleus accumbens, the brain’s reward center, and curbs an animal’s urge for sustenance.
X chromosome inactivation; motor difficulties in 16p11.2 duplication and deletion; oligodendroglia
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 6 May.
X chromosome inactivation; motor difficulties in 16p11.2 duplication and deletion; oligodendroglia
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 6 May.
Decoding flies’ motor control with acrobat-scientist Eugenia Chiappe
The tiny performers steal the show in Chiappe’s sensorimotor-integration lab in Lisbon, Portugal.

Decoding flies’ motor control with acrobat-scientist Eugenia Chiappe
The tiny performers steal the show in Chiappe’s sensorimotor-integration lab in Lisbon, Portugal.