Analysis unearths common genetic roots for disparate traits
Using a new genetic approach, researchers are finding shared risk factors for seemingly unrelated conditions, ranging from autism to obesity.

Using a new genetic approach, researchers are finding shared risk factors for seemingly unrelated conditions, ranging from autism to obesity.

An analysis of blood samples from nearly 17,000 individuals with autism points to new regions of the genome likely to be involved in the disorder.
DNA sequences called enhancers — which boost the expression of genes from within or outside them — are enriched for genetic variants linked to autism, suggests a new study. The finding may help researchers understand how variants outside genes contribute to autism.

After eight years of prominence as an autism risk gene, a new analysis significantly brings down CNTNAP2’s importance in the disorder: According to the study, rare mutations in a single copy of the gene are unlikely to cause autism.
A new computational approach predicts how sequence variations in both the coding and noncoding regions of a gene affect the gene’s expression. The method, described today in Science, may help researchers understand how specific variants contribute to disorders such as autism.

Researchers are taking a second look at dozens of autism candidate genes, sequencing them in thousands of individuals to bolster the evidence linking them to autism.

Researchers have analyzed more than 90,000 exomes — the protein-coding regions of the genome — the largest such set yet, they announced Monday at the American Society of Human Genetics Annual Meeting in San Diego. The resource gives scientists an invaluable tool to probe the significance of specific mutations.
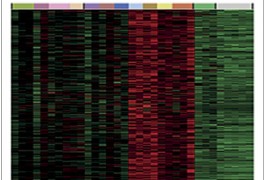
Much of the genetic risk for autism may reside in regulatory regions of the genome, hidden from traditional methods of sequence analysis. That’s the upshot of preliminary results from three studies presented yesterday at the American Society of Human Genetics Annual Meeting in San Diego.
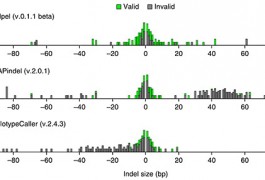
A new algorithm accurately detects large DNA insertions and deletions in the protein-coding regions of the genome.
New estimates on the role of common mutations in autism raise questions about how to quantify and parse genetic risk. Three experts say both common and rare variants are worth pursuing.