Serotonin
Neurotransmitter switch-up helps fan extreme stress into full-blown fear
The flip occurs when certain neurons in the dorsal raphe start to express the chemical GABA instead of glutamate, a new study shows.

Neurotransmitter switch-up helps fan extreme stress into full-blown fear
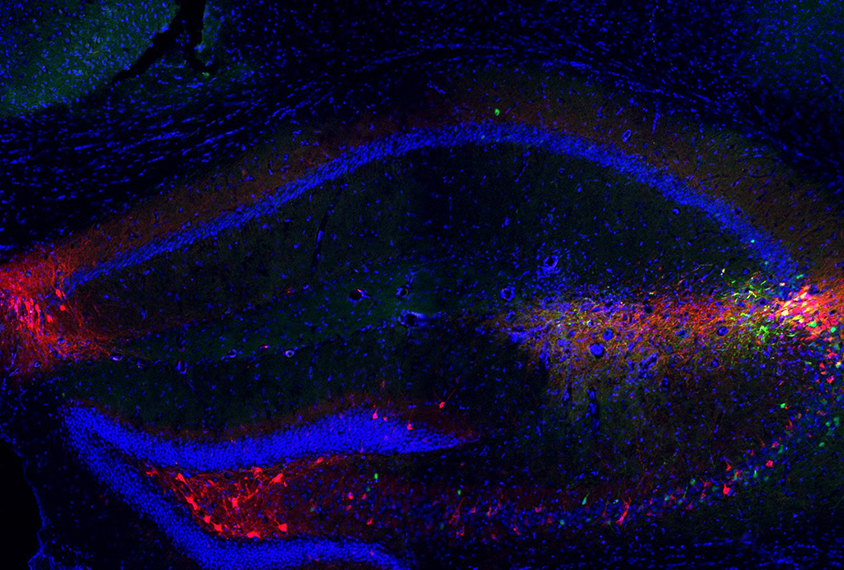
Serotonin powers pruning of developing brain circuits in mice
Mice with microglia missing receptors for the neurotransmitter serotonin since birth have too many synapses and show social difficulties in adulthood.
Serotonin powers pruning of developing brain circuits in mice
Serotonin initiates earliest social bonds
Mice and rats, for example, gravitate toward their mother’s bedding over bedding that is clean or smells of a different dam.
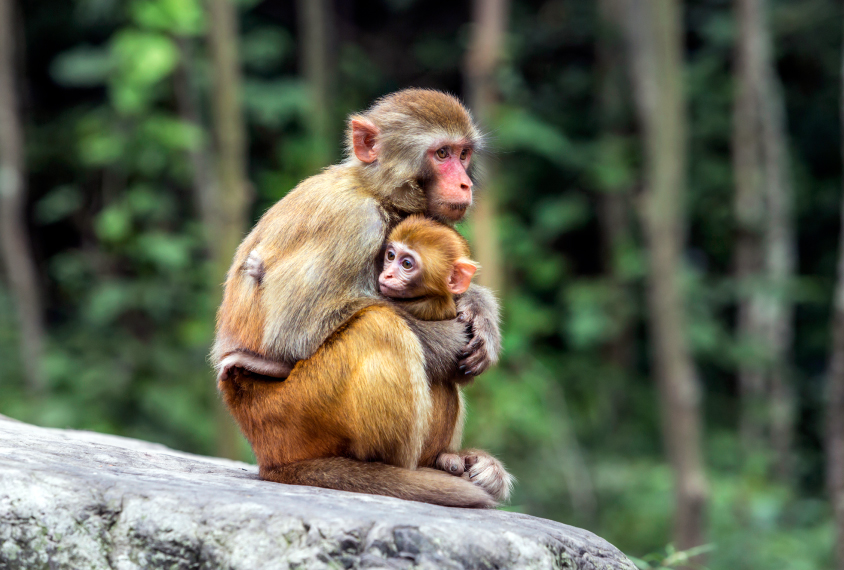

Serotonin initiates earliest social bonds
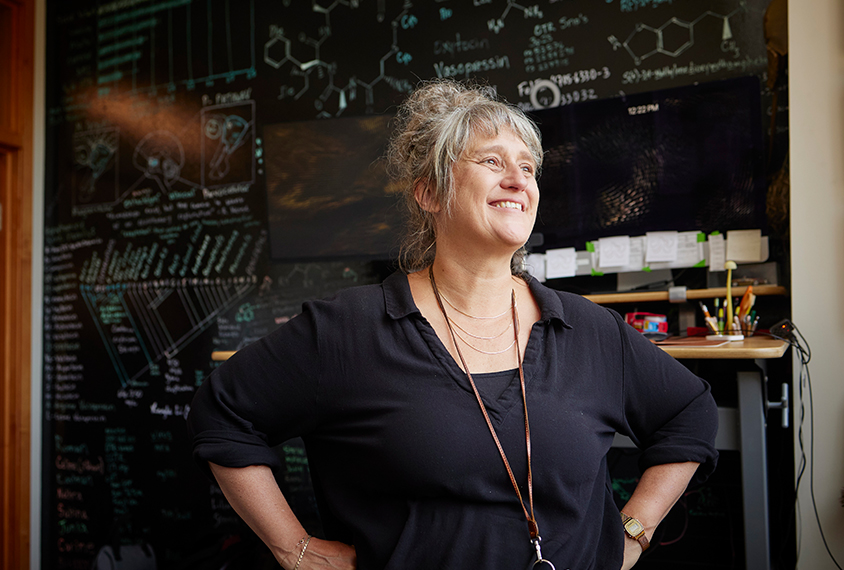
In deep water with Gül Dölen
A researcher's existential crisis led to a scientific breakthrough.
Tripping over the potential of psychedelics for autism
Drugs such as LSD act primarily on the serotonin system, which is implicated in autism — and some autistic people who experiment with psychoactive compounds report enhanced social connections, among other benefits. But researchers have more questions than answers.

Tripping over the potential of psychedelics for autism
Serotonin shapes social memory signals
Social memory, which may be altered in autism, depends on serotonin-sensitive neurons that send signals from the medial septum to the hippocampus.
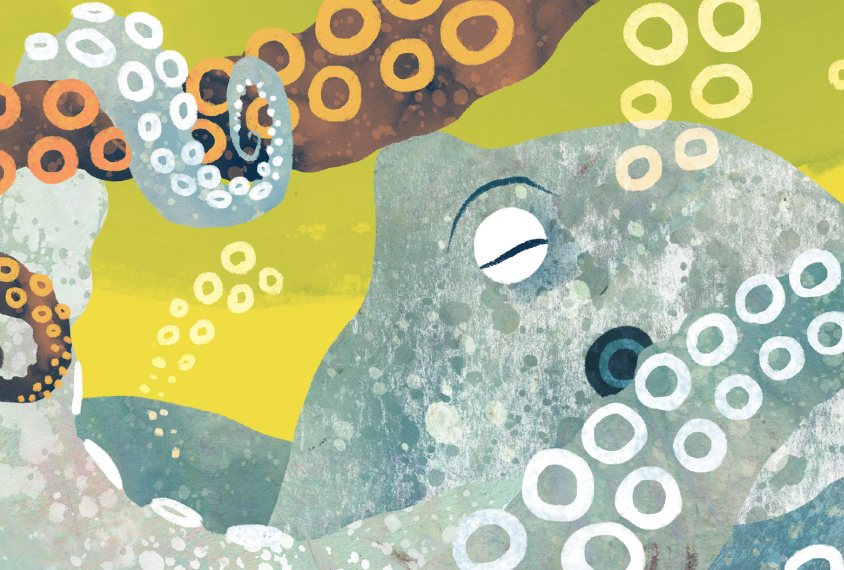
Getting eight arms around autism
Octopuses can solve some of the same problems as people but do so in unusual ways.
Drugs boost serotonin, socialization in multiple autism mouse models
The finding that MDMA and an experimental serotonin agonist increase sociability across six different model mice suggests that disparate autism-linked mutations converge on the same underlying pathways.
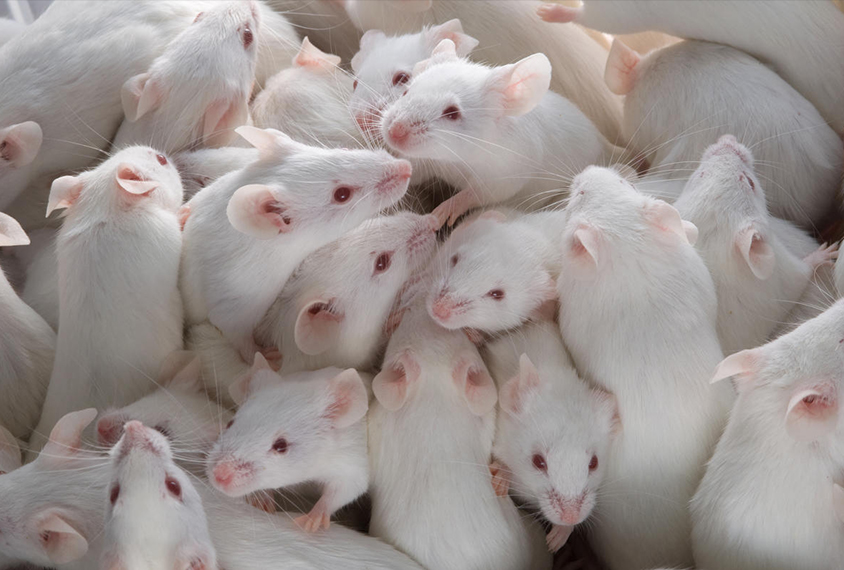

Drugs boost serotonin, socialization in multiple autism mouse models
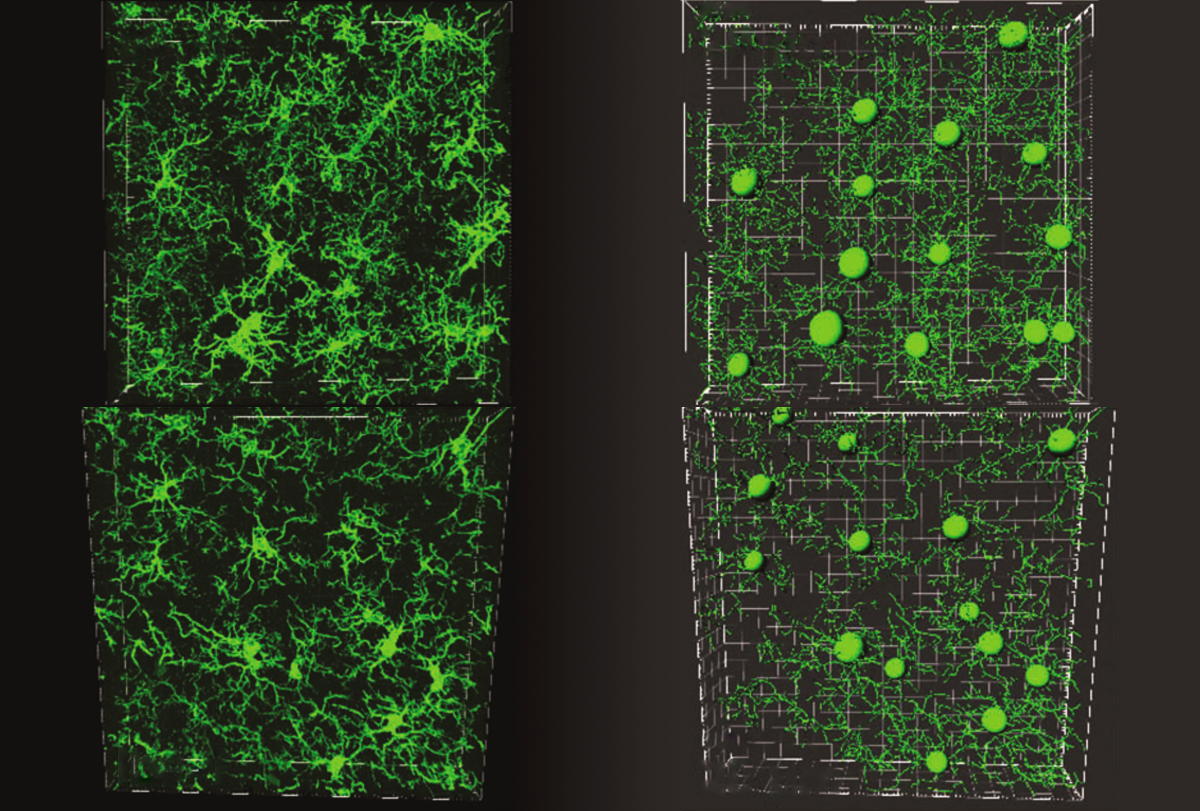
After 60 years, scientists are still trying to crack a mysterious serotonin-autism link
The high levels of serotonin seen in the blood of some autistic people have confounded scientists for more than half a century. Despite so little progress, some researchers refuse to give up.
After 60 years, scientists are still trying to crack a mysterious serotonin-autism link
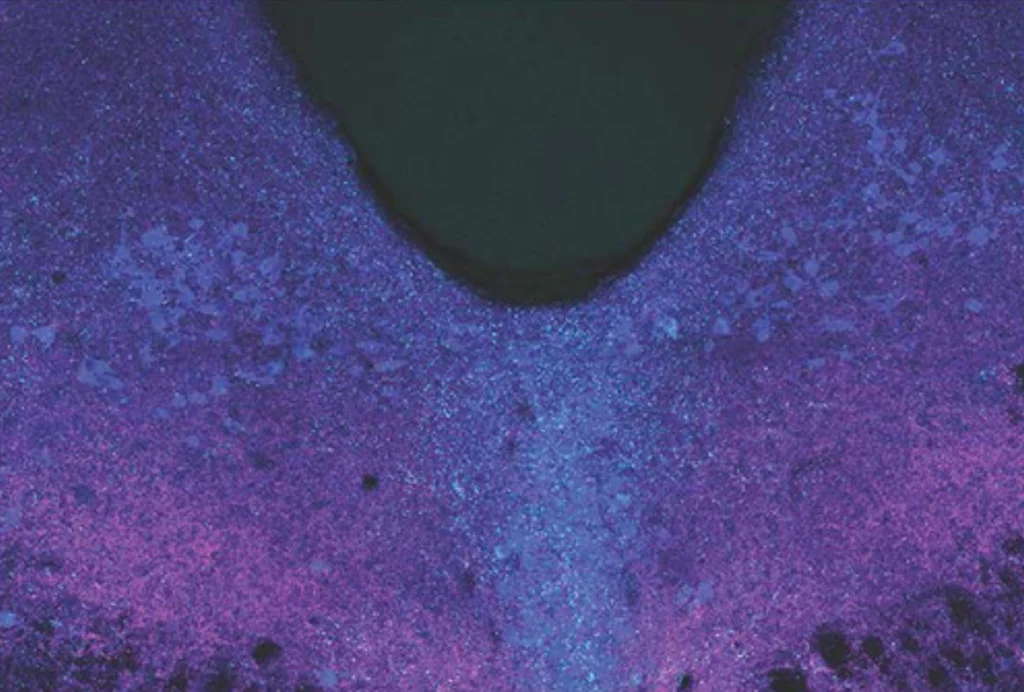
Sensor helps scientists spy on serotonin activity in mice in real time
A glowing protein tracks serotonin levels and location in the brains of living mice and could yield clues to the neurotransmitter’s role in autism.
Sensor helps scientists spy on serotonin activity in mice in real time
Explore more from The Transmitter
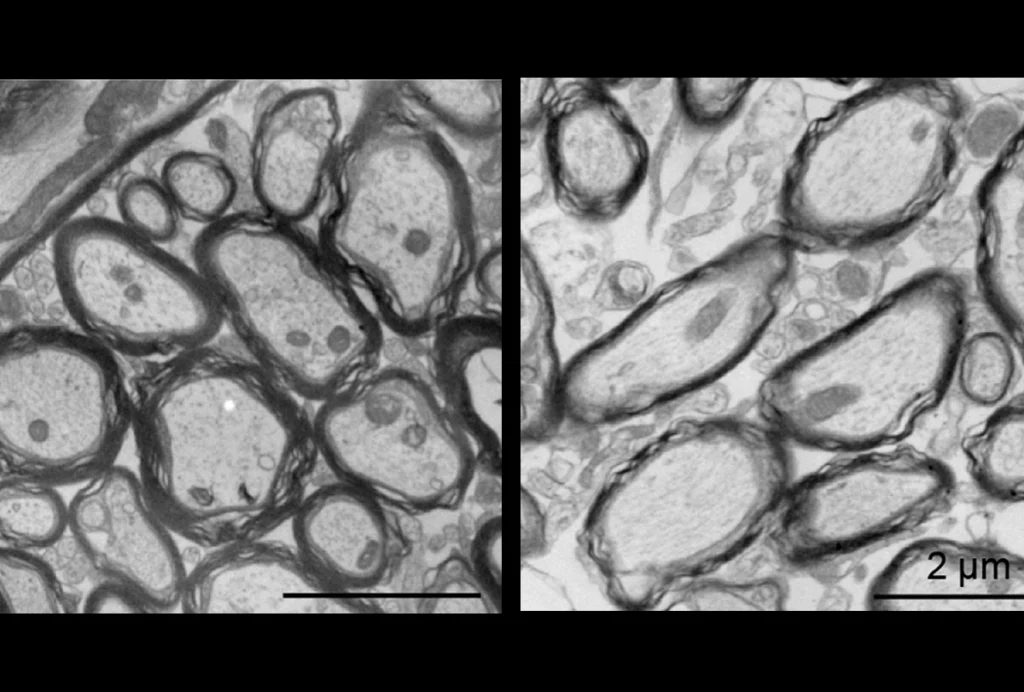
X chromosome inactivation; motor difficulties in 16p11.2 duplication and deletion; oligodendroglia
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 6 May.
X chromosome inactivation; motor difficulties in 16p11.2 duplication and deletion; oligodendroglia
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 6 May.
Decoding flies’ motor control with acrobat-scientist Eugenia Chiappe
The tiny performers steal the show in Chiappe’s sensorimotor-integration lab in Lisbon, Portugal.

Decoding flies’ motor control with acrobat-scientist Eugenia Chiappe
The tiny performers steal the show in Chiappe’s sensorimotor-integration lab in Lisbon, Portugal.
Neuroscience needs a research-video archive
Video data are enormously useful and growing rapidly, but the field lacks a searchable, shareable way to store them.
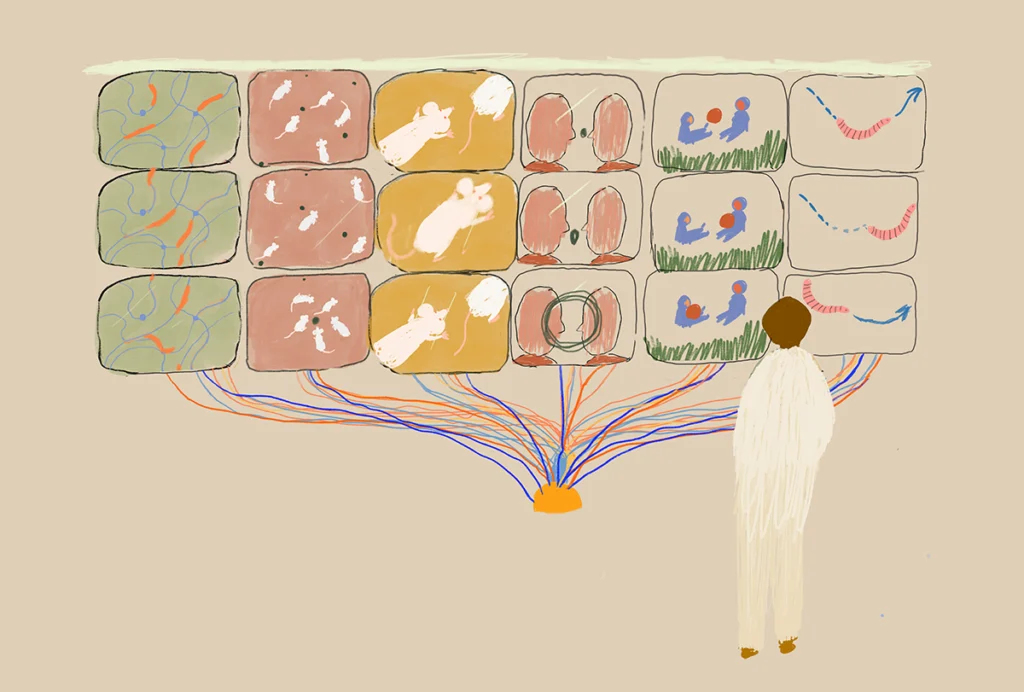
Neuroscience needs a research-video archive
Video data are enormously useful and growing rapidly, but the field lacks a searchable, shareable way to store them.