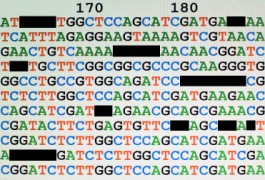
Large sequencing study ties autism genes to fragile X
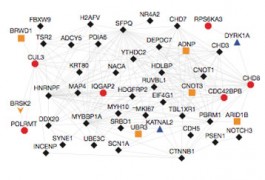
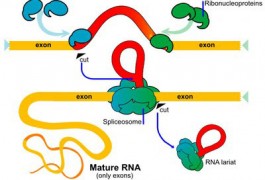
Children with autism carry twice as many new and damaging genetic mutations as typically developing children, according to a new study published in Neuron. The researchers also identified intriguing genetic links between autism and fragile X syndrome.