Control of gene expression alters impact of autism mutations
Variants that control gene expression are often involved in whether a mutation ends up being harmful, and how harmful it is.

Variants that control gene expression are often involved in whether a mutation ends up being harmful, and how harmful it is.

Software to identify genetic variants, along with a new synthetic human genome, could help scientists discover mutations associated with conditions such as autism.

Watch the complete replay of this journal club, which featured a paper exploring rare genetic variation in psychiatric conditions, including autism.

We must diversify databases of reference DNA to improve our ability to interpret the consequences of genetic variation.
A mouse model based on exposure to an epilepsy drug offers a useful window into the brain circuits altered in autism.
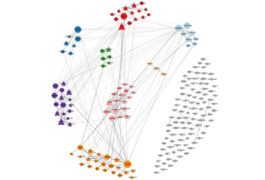
An algorithm combs through genetic data to identify variants involved in autism and four other brain conditions.

Autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder often coincide, but the search for common biological roots has turned up conflicting evidence.

This year’s list of top papers highlights nuances in the genetics of autism and new leads on early treatment.
A monkey study suggests facial recognition is not innate, a puzzle piece symbol carries negative connotations, and scientists are using a federal law to snoop on colleagues.
A Tampa clinic goes rogue with fecal transplants, autism’s genetic ancestry traces to our deep past, and the U.S. Supreme Court revives the travel ban.