Monkey study bolsters case for brain hormone’s role in autism
Male monkeys that avoid touching, grooming or playing with others have low brain levels of the hormone vasopressin.

Male monkeys that avoid touching, grooming or playing with others have low brain levels of the hormone vasopressin.
Families need more support from researchers in order for their heroic efforts to be optimally effective.

The activity of a set of proteins in the blood may distinguish people with autism from those without the condition.
Decoding distortions in the brain’s largest nerve tract could lay bare basic problems with long-range neural connections in autism.

A surprising number of genes associated with autism also have links to cancer. Does that mean cancer drugs can treat autism?
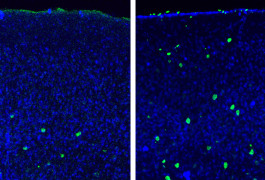
Researchers are beginning to understand how mutations in a cancer-linked pathway called WNT contribute to autism.
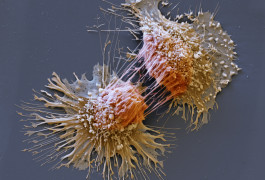
A comprehensive catalog of the genes that show ties to both autism and cancer highlights the role of cell growth in both conditions.
The brain enlargement seen in many children with autism may reveal hints about the condition’s causes.

The same autism-linked mutation can lead to dramatically different behaviors in rats and mice.
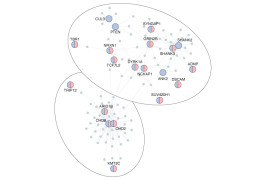
Two studies prioritize autism risk genes for further research and illuminate how different types of mutations may work together.