Molecular mechanisms: Brain antibodies alter mouse behavior
Rare antibodies taken from mothers of children with autism lead to developmental delay and anxiety in mouse pups, according to a study published 27 August in the Journal of Neuroimmunology.

Rare antibodies taken from mothers of children with autism lead to developmental delay and anxiety in mouse pups, according to a study published 27 August in the Journal of Neuroimmunology.
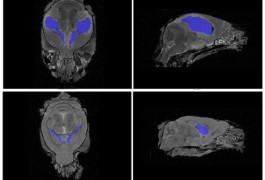
Mice with elevated levels of the immune molecule interleukin-6 have abnormally large brains, according to a study published 23 August in the International Journal of Neuroscience.
Children diagnosed with autism tend to have low blood levels of several immune molecules at birth, according to an epidemiological study published in August in the Journal of Immunology.

Prenatal exposure to antibodies collected from the mothers of children with autism boosts stem cell proliferation in the brains of mice, according to two studies presented at the 2012 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in New Orleans.
Treatment with a single bacterial species curbs anxiety and repetitive behaviors and boosts vocalizations in a mouse model of autism, according to a poster presented Monday at the 2012 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in New Orleans.

The so-called ‘spiny mouse’ species has a gestational period twice as long as that of typical laboratory mice. This makes them good models for studying the link between prenatal exposure and autism risk, according to a study published 29 August in Brain, Behavior and Immunity.
As the central organ regulating maternal-fetal interactions, the placenta is perfectly positioned to mediate environmental and genetic risk factors during prenatal development. It may also relay risk factors for autism to the fetus, says Paul Patterson.
Traditional prenatal testing cannot distinguish between large disruptive chromosomal duplications and multiple harmless repeats, according to a study published 25 July in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
Undergoing fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization, does not increase the risk of having a child with autism, according to two epidemiology studies published this July.

Genes and the environment each influence the role of the other in determining the risk of developing autism. Genetics can determine how susceptible one is to the environment, and environmental factors can influence gene expression and introduce mutations, says immunologist Janine LaSalle.