Molecular mechanisms: MeCP2 regulated by chemical switch
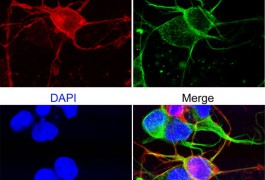
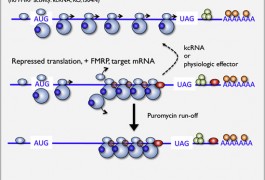
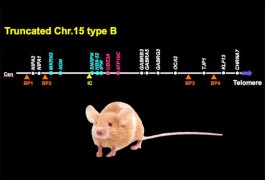
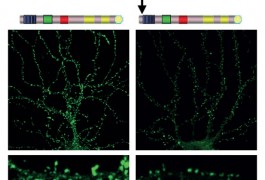
MeCP2, the protein missing in people with Rett syndrome, enhances learning and memory by binding to key genes and either activating or inhibiting their expression, according to a study published 17 July in Nature Neuroscience. Adding a phosphate to the protein in response to neuronal activity releases MeCP2 from these genes, the study found.