Molecular mechanisms: Study links excess protein to autism
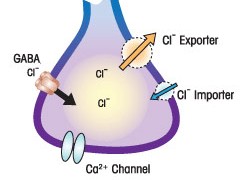
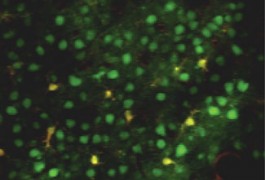
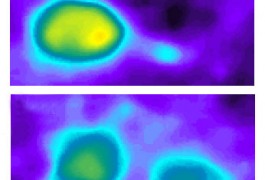
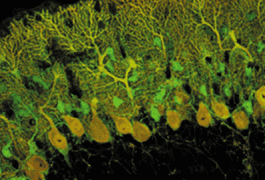
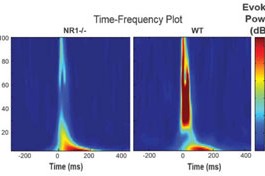
Elevated levels of EIF4E, which plays a key role in protein synthesis, lead to autism-like behaviors and abnormal neuronal signaling in mice, according to a study published 17 January in Nature.