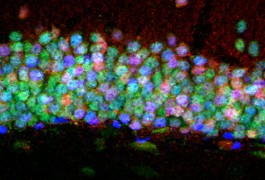
Mouse models point to early troubles in tuberous sclerosis
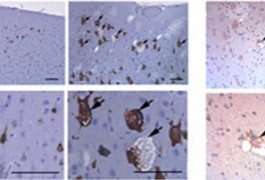
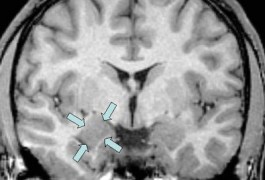
The brain abnormalities characteristic of tuberous sclerosis may begin early in development and involve malfunctioning of neuronal precursors, according to studies of two different mouse models of the disorder published in October.