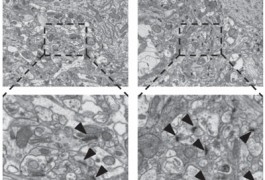
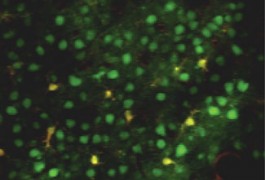
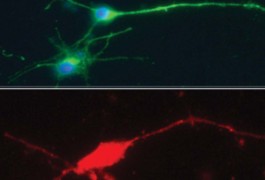
Molecular mechanisms: Rats could model autism gender bias
Prenatal exposure of rats to the epilepsy drug valproic acid leads to behavioral and brain features that resemble autism, in males more than in females, according to a study published in the March issue of the Journal of Neurochemistry.