Social interactions not rewarding for children with autism
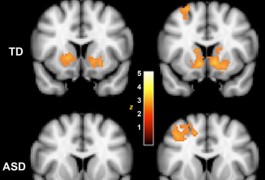
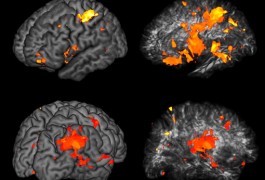
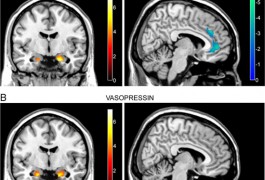
Children with autism have abnormally low brain activity in the ‘reward center’ of the brain when given money or shown a happy face, according to a study in Autism Research. These are the first imaging data to support the notion that children with autism derive less pleasure from social interactions compared with their healthy peers.