Blood pressure drug may protect brain from seizures
A blood pressure drug called bumetanide may shield the brain from the effects of severe seizures early in life.

A blood pressure drug called bumetanide may shield the brain from the effects of severe seizures early in life.

For 2014, rather than compile the ‘top tools and techniques’ — a list certain to include CRISPR and other technical tricks detailed in our weekly Toolboxes — we asked researchers to dream up the next big tool in autism research. Their wishes range from protein sequencers to scanners that can capture brain activity during daily activities.
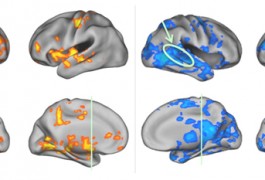
Pivotal response treatment, an effective form of behavioral therapy for autism, normalizes brain activity in children with the disorder, according to a small study published earlier this month in Brain Imaging and Behavior. This suggests that brain imaging can signal early responses to autism treatments.
Soft touch and physical closeness to other people wire the social brain right from the earliest days after birth, and problems in the response to touch may play a fundamental role in autism. This picture emerges from unpublished results presented by several teams at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
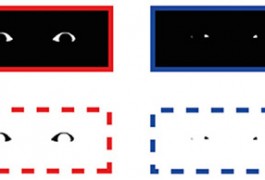
By 7 months of age, babies can subconsciously discriminate between happy and fearful emotions by looking only at the eyes of another person, suggest results presented at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
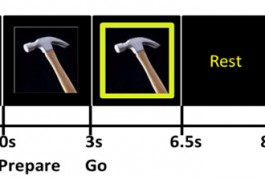
Children with autism show different patterns of brain activity during everyday gestures and movements than controls do, suggest unpublished results presented today at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Many studies have found differences in the brains of young infants later diagnosed with autism. But to call this a biomarker requires independent validation, time and patience, says Helen Tager-Flusberg.

Deleting MeCP2 from a subset of neurons that mediate inhibitory signals recapitulates many of the symptoms of Rett syndrome in mice. Conversely, expressing the gene only in that subset, but not in the rest of the brain, protects the mice from some of those same symptoms. The results were published last week in Nature Neuroscience.

Mirror neurons, which fire when a person performs or observes an action, function just as well in young children with autism as they do in their typically developing peers. The finding, reported 10 February in Autism Research, boosts evidence against a popular theory of autism.

Three studies published over the past two months have found significant evidence that children and adolescents with autism have brains that are overly connected compared with the brains of controls. The findings complicate the theory that autism is fundamentally characterized by weakly connected brain regions.