Family groups play key role in advancing autism research
Families need more support from researchers in order for their heroic efforts to be optimally effective.
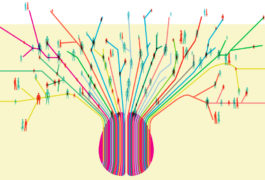
Families need more support from researchers in order for their heroic efforts to be optimally effective.
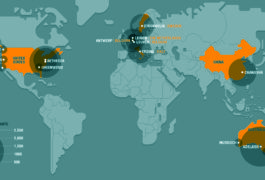
A massive sequencing study spanning seven countries links 38 new genes to autism and developmental delay.

A surprising number of genes associated with autism also have links to cancer. Does that mean cancer drugs can treat autism?


Harmful mutations in autism genes crop up in Chinese individuals about as often as they do in people of European ancestry.

Mice missing one copy of a top autism gene show many of the features seen in people with the mutation — but not social deficits.
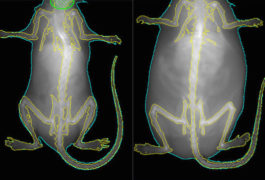
Subsets of neurons lacking a gene called RAI1 contribute to Smith-Magenis syndrome, a rare condition related to autism.
Mutations in one of the strongest autism candidate genes may block the proliferation of neurons during development.
Mice lacking one copy of CHD8, a key autism gene, show signs of social deficits and broad changes in gene expression.
A gene that has strong ties to autism controls the expression of many other autism candidates.