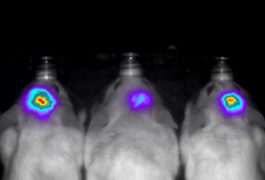
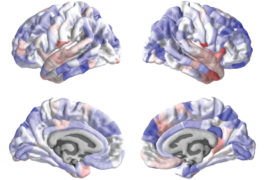
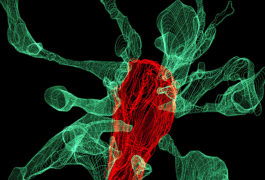
Randomized trial repository; Beijing brain center; global science march and more
Scientists release a list of all randomized controlled trials of autism treatments, China establishes a brain center for an ambitious new project, and people around the world march for science again.