Subgroups improve genetic analysis of autism
Researchers can increase the power of studies that link genetic variants to autism by factoring in potential subgroups of the disorder, according to a report published 26 June in PLoS One.
Emerging tools and techniques that may advance autism research.
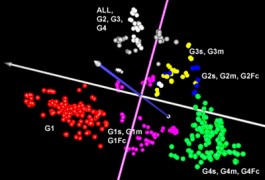
Researchers can increase the power of studies that link genetic variants to autism by factoring in potential subgroups of the disorder, according to a report published 26 June in PLoS One.

A new clinical test for duplications or deletions of chromosomal regions is customized to detect more than 380 known changes, including many that are linked to autism. The method was published 24 June in the American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A.
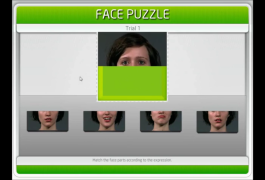
A clever new test assesses whether someone with autism can recognize emotions from facial expressions without needing to name them. The test was described in the 26 June issue of Frontiers in Psychology.

Using a portable mat embedded with pressure sensors, researchers have shown that adults with severe autism walk more slowly than controls do. The results were published 20 May in Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience.
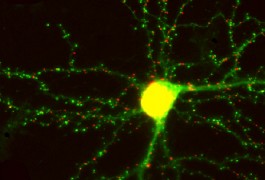
Researchers have found a new way to light up proteins in living cells, revealing the connections between neurons, according to a study published 19 June in Neuron.

A new software tool detects chromosomal alterations present in only a subset of cells in the body. This method, described 31 May in BMC Genomics, may help reveal mosaicism’s contribution to neurological disorders.
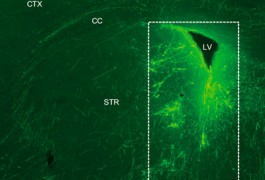
A new technique to transform human stem cells into neurons is faster, more efficient and more reliable than existing methods, according to a study published 5 June in Neuron.
By combining bioinformatics techniques with an analysis of gene expression, researchers have identified 30 candidate genes for autism, according to a study published 28 May in Translational Psychiatry.

Screening the genome for small chromosomal abnormalities may identify potential genetic causes of autism or intellectual disability in 16 percent of children tested, according to a study published 24 May in the European Journal of Paediatric Neurology.

To study attention in people with autism during complex social situations, researchers have developed a virtual reality version of public speaking, according to a study published 20 May in Autism Research.