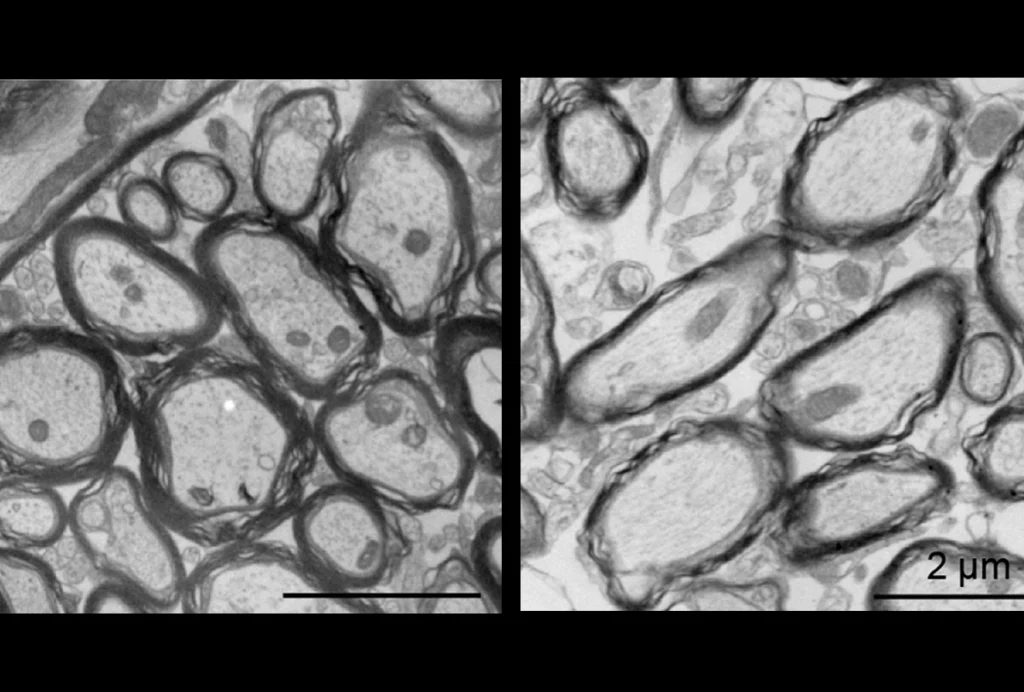
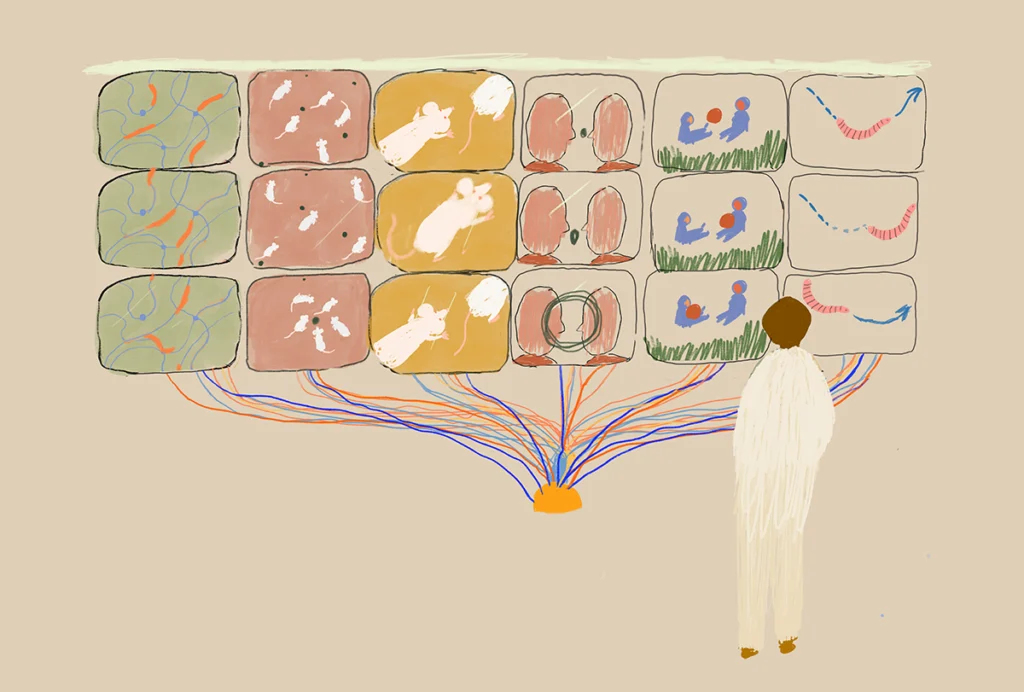
This article is more than five years old.
Neuroscience—and science in general—is constantly evolving, so older articles may contain information or theories that have been reevaluated since their original publication date.