Research roundup
- Autistic youth make up 11.5 percent of all the adolescents admitted to two psychiatric facilities in Canada, where 1.5 percent of the general population is autistic. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- Autistic and non-autistic children show similar visual-gaze responses to facial expressions of emotions when the emotion strength increases over time, but they respond differently when strong emotions are presented early in a sequence. Autism Research
- Rats prenatally exposed to valproic acid, a model of autism, have altered microbiota and lower levels of short-chain fatty acids in their gastrointestinal tract compared with control rats, and associated changes in brain neurotransmitters. Frontiers in Physiology
- Autistic people often have severe visual impairment for which early interventions can be helpful. Journal of Public Health Research
- The Depression Anxiety Stress Scales-21 outperforms the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale-Revised in assessing symptoms of mood disorders in autistic people. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- Early interventions in children with autism or at an elevated likelihood of the condition have limited impact on neurodevelopmental outcomes, according to a review of clinical studies. Autism Research
- A phospholipid imbalance during mid-pregnancy and dysregulation of many more metabolites at birth may serve as biomarkers for autism, according to a metabolomic analysis of blood. Molecular Psychiatry
- Mice missing the autism-linked gene CSMD3 display altered sociability, repetitive behaviors and motor problems, as well as changes in the form and function of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Journal of Neuroscience
- Autistic girls, like non-autistic girls, use more words and speak more quickly than their male peers. Molecular Autism
- Autistic young people with genetic variants strongly linked to the condition tend to have more sensory issues than those without identified genetic contributors. Journal of Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders
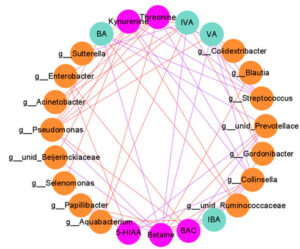 Gut-brain axis: Bacterial species in the gut, and their short-chain fatty acid metabolites, appear to affect brain neurotransmitter levels in an animal model of autism.
Gut-brain axis: Bacterial species in the gut, and their short-chain fatty acid metabolites, appear to affect brain neurotransmitter levels in an animal model of autism.
Science and society
- The authors of a 2017 journal article that claimed brain imaging in combination with machine learning could predict suicidality have retracted the study. The lead author, Marcel Adam Just, co-wrote a Spectrum opinion piece on imaging brain connectivity in autism in 2013. Retraction Watch
- Early-career autism researchers may find opportunities by shifting their focus to align with the autism community’s stated needs, writes Diana Weiting Tan in a commentary. Autism in Adulthood
- Genetic testing should be offered more widely, as genetic diagnoses can help families of children with neurodevelopmental conditions seek better treatment and find community, writes a physician parent of a child with a CACNA1A-related disorder. STAT
- More girls are being diagnosed with autism than in the past, but so are more women — leading some to wonder how many girls are still being missed. The New York Times
- Rutgers University faculty unions, which include adjunct faculty and graduate students, are striking after year-long negotiations over salaries. NJ.com