Research roundup
- The prefrontal cortex may manage cognitive flexibility by monitoring feedback via specific neuronal pathways, according to a study in mice. Cell
- Clinical differences do not explain the racial disparities in age at autism diagnosis; Black and white children referred for evaluation have similar cognitive and behavioral profiles. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders
- Being near other people causes non-autistic people to shrink their personal space and modulate their sensory integration; autistic people, however, tend to maintain personal space and sensory responsiveness in social settings. Biological Psychiatry
- Training doctors to use a web-based autism screen may increase screening at routine checkups and boost the clinicians’ confidence around autism care. Academic Pediatrics
- Autism traits can emerge, increase, decrease or dissipate from childhood through adolescence, according to a population-based study. American Journal of Psychiatry
- Looking at COVID-19 in pregnant women provides a new opportunity to study how viral infection can affect fetal brain development. STAT
- Researchers have compiled case reports of 62 people to characterize FOXP1 syndrome, in which mutations of the FOXP1 gene cause developmental delays, autism or intellectual disability. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- Several gene therapies targeting some of the most common variants linked to autism are inching closer to clinical trials. Nature Biotechnology
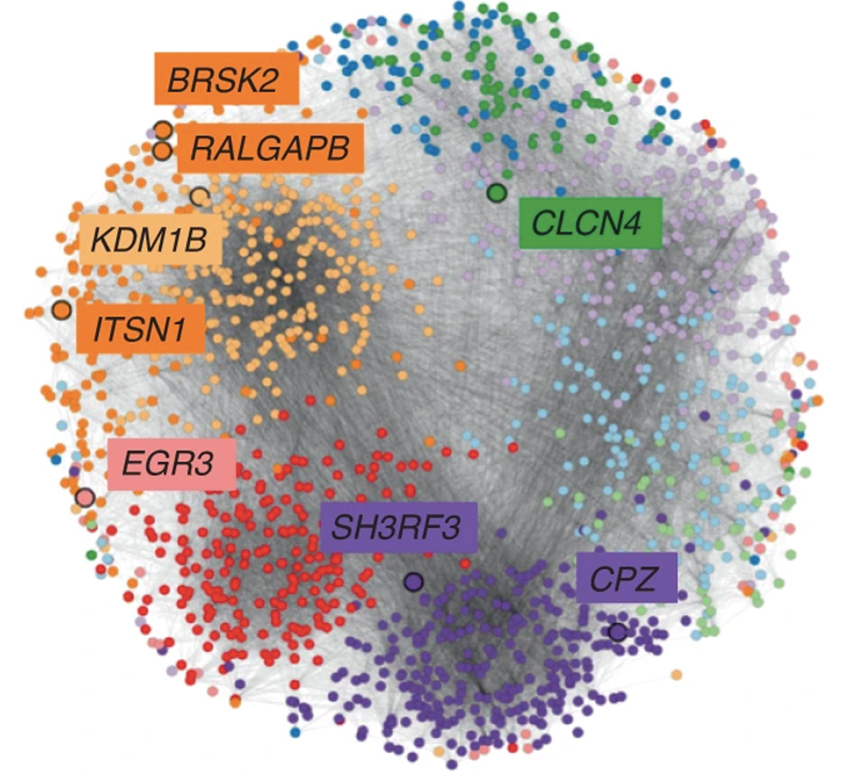 Network analysis: Grouping autism-linked genes according to their biological functions may help researchers develop gene therapies.
Network analysis: Grouping autism-linked genes according to their biological functions may help researchers develop gene therapies. - After careful screening, researchers estimate that 1.53 percent of children in Tarragona, Spain, have autism — nearly doubling a previous estimate. Autism
- Molecular tools that enable researchers to image dopamine function in people may help scientists better understand conditions such as autism and schizophrenia. Cell Chemical Biology
Science and society
- The Autistic Self Advocacy Network has commented on the conviction of former police officer Derek Chauvin, re-asserting its commitment to making a safer, more just world for those in marginalized groups. Autistic Self Advocacy Network
- Laboratories continue to struggle with shortages of personal protective equipment, pipette tips, freezers and reagents because of the coronavirus pandemic. The Scientist
- Neuroscientist Ranulfo Romo Trujillo has left his academic post at the National Autonomous University of Mexico in the wake of sexual harassment allegations. Science
- Autism services and lifespan issues receive less than 10 percent of federal research funding in the United States, despite an advisory panel’s recommendation that these areas be prioritized. Disability Scoop